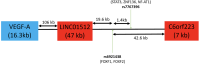
VEGF-A cis-located SNPs on human chromosome 6 associated with VEGF-A plasma levels and survival in a coronary disease cohort
- PMID: 40247170
- PMCID: PMC12004769
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-025-04751-3
VEGF-A cis-located SNPs on human chromosome 6 associated with VEGF-A plasma levels and survival in a coronary disease cohort
Abstract
Background: Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death worldwide. Risk stratification of CVD patients may be improved by predictive biomarkers, including genetic markers. Elevated circulating vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) levels have been linked to CVD development. We explored whether single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) at the VEGFA locus on human chromosome 6 were associated with VEGF-A levels and clinical outcomes in established CVD. VEGF-A levels were compared between coronary heart disease patients and heart healthy controls.
Methods: Imputed genotypes of 30 SNPs from the VEGFA region for 1935 patients from the Coronary Disease Cohort Study (CDCS) and 1183 individuals from the Canterbury Healthy Volunteers Study (HVOL) were analysed for associations with cardiometabolic parameters. Association with clinical endpoints was assessed using Kaplan-Meier analysis and multivariate regression models. To validate the findings from imputed data, DNA samples of 2027 CDCS patients and 227 HVOL participants were manually genotyped for variants rs6921438 and rs7767396. Baseline plasma VEGF-A assayed by ELISA in 227 HVOL participants was compared with levels in 549 CDCS patients.
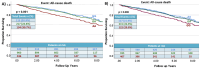
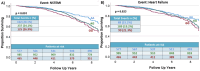
Results: Manual genotyping showed rs6921438 AA and rs7767396 GG genotype groups had lower VEGF-A levels at baseline (CDCS: rs6921438 AA (27.7 pg/mL), AG (43.3 pg/mL), GG (63.2 pg/mL), p = 4.49 × 10- 22; rs7767396: GG (27.4 pg/mL), AG (42.8 pg/mL), AA (61.5 pg/mL) p = 3.47 × 10- 21; HVOL rs6921438 AA (12.8 pg/mL), GA (19.9 pg/mL), GG (26.4 pg/mL) p = 0.021; rs7767396 GG (12.6 pg/mL), AG (19.6 pg/mL), AA (25.9 pg/mL) p = 0.029). In the CDCS cohort rs6921438 AA was associated with increased risk of all-cause death (p = 0.03); non ST-elevated myocardial infarction (NSTEMI, p = 0.0003), heart failure (HF, p = 0.035) and major adverse cardiovascular events (p = 0.032); rs7767396 GG was associated with increased NSTEMI (p = 0.001) and HF (p = 0.023) risk; rs6921438 AA (Hazard Ratio (HR) = 6.55 p = 0.017), rs7767396 GG (HR = 0.149, p = 0.017) and VEGF-A (HR = 2.55, p = 0.018) were independent HF admission risk predictors.
Conclusions: Variants rs6921438 and rs7767396 are associated with plasma VEGF-A levels. Both SNPs and VEGF-A may be useful in prognosis for HF after acute coronary events.
Keywords: Outcome; Prognosis; Single nucleotide polymorphism; Vascular endothelial growth factor; rs6921438; rs7767396.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Human ethics and consent to participate: The CDCS study was approved by the New Zealand (NZ) Multi-Region Ethics Committee, retrospectively registered at the Australian New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry (ACTRN12605000431628 on 16 September 2005), and all participating patients provided written, informed consent. The HVOL study was approved by the New Zealand Health and Disability Ethics Committee (Reference CTY/01/05/062) and registered with the Australian New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry (ACTRN1260500448640). All participating patients provided written, informed consent. Both studies conform to the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki and Title 45, U.S. Code of Federal Regulations, Part 46. Consent for publication.: Not applicable – this article does not report an individual participant’s data in any form. Competing interests: B.R.P. is a Senior Editorial Board Member of BMC Cardiovascular Disorders.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Plasma soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1, placental growth factor, and vascular endothelial growth factor system gene variants as predictors of survival in heart failure.Eur J Heart Fail. 2024 Aug;26(8):1804-1813. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.3368. Epub 2024 Jul 9. Eur J Heart Fail. 2024. PMID: 38980212
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-related polymorphisms rs10738760 and rs6921438 are not risk factors for proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2019 Feb 12;19(1):94-100. doi: 10.17305/bjbms.2018.3519. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 30579324 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Genetic Polymorphisms on VEGFA and VEGFR2 With Risk of Coronary Heart Disease.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 May;95(19):e3413. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003413. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27175642 Free PMC article.
-
Association of rs6921438 A<G with serum vascular endothelial growth factor concentrations in patients with metabolic syndrome.Gene. 2018 Aug 15;667:70-75. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.05.017. Epub 2018 May 4. Gene. 2018. PMID: 29733969
-
The effect of single nucleotide polymorphisms on depression in combination with coronary diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Apr 30;15:1369676. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1369676. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38745947 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

