Radiomics analysis of dual-layer detector spectral CT-derived iodine maps for predicting Ki-67 PI in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 40247246
- PMCID: PMC12007212
- DOI: 10.1186/s12880-025-01664-7
Radiomics analysis of dual-layer detector spectral CT-derived iodine maps for predicting Ki-67 PI in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the feasibility of radiomics analysis using dual-layer detector spectral CT (DLCT)-derived iodine maps for the preoperative prediction of the Ki-67 proliferation index (PI) in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC).
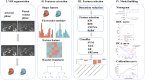
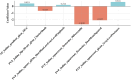
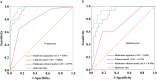
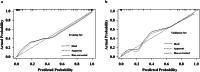
Materials and methods: A total of 168 PDAC patients who underwent DLCT examination were included and randomly allocated to the training (n = 118) and validation (n = 50) sets. A clinical model was constructed using independent clinicoradiological features identified through multivariate logistic regression analysis in the training set. The radiomics signature was generated based on the coefficients of selected features from iodine maps in the arterial and portal venous phases of DLCT. Finally, a radiomics-clinical model was developed by integrating the radiomics signature and significant clinicoradiological features. The predictive performance of three models was evaluated using the Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve and Decision Curve Analysis. The optimal model was then used to develop a nomogram, with goodness-of-fit evaluated through the calibration curve.
Results: The radiomics-clinical model integrating radiomics signature, CA19-9, and CT-reported regional lymph node status demonstrated excellent performance in predicting Ki-67 PI in PDAC, which showed an area under the ROC curve of 0.979 and 0.956 in the training and validation sets, respectively. The radiomics-clinical nomogram demonstrated the improved net benefit and exhibited satisfactory consistency.
Conclusions: This exploratory study demonstrated the feasibility of using DLCT-derived iodine map-based radiomics to predict Ki-67 PI preoperatively in PDAC patients. While preliminary, our findings highlight the potential of functional imaging combined with radiomics for personalized treatment planning.
Keywords: Dual-layer detector spectral computed tomography; Iodine map; Ki-67; Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; Radiomics.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The research adhered to the Declaration of Helsinki and its latest amendments. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of Chongqing General Hospital (approval number KY S2023-070-01), and the need for informed consent was waived owing to the retrospective study design. Funding: This study was supported by the Medical Research Program of the combination of Chongqing National Health Commission and Chongqing Science and Technology Bureau, China (2024QNXM058) and the Key Special Program of Technological Innovation and Application Development in Chongqing, China (no. CSTB2023TIAD-KPX0059-2). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Development of a CT radiomics nomogram for preoperative prediction of Ki-67 index in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: a two-center retrospective study.Eur Radiol. 2024 May;34(5):2934-2943. doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-10393-w. Epub 2023 Nov 8. Eur Radiol. 2024. PMID: 37938382
-
Development and validation of a model based on preoperative dual-layer detector spectral computed tomography 3D VOI-based quantitative parameters to predict high Ki-67 proliferation index in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Insights Imaging. 2024 Dec 5;15(1):291. doi: 10.1186/s13244-024-01864-9. Insights Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39636501 Free PMC article.
-
A clinical-radiomics nomogram based on dual-layer spectral detector CT to predict cancer stage in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Cancer Imaging. 2024 May 9;24(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s40644-024-00700-z. Cancer Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38725034 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics and deep learning models for CT pre-operative lymph node staging in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Radiol. 2024 Jul;176:111510. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2024.111510. Epub 2024 May 18. Eur J Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38781919
-
The clinical applications of dual-layer spectral detector CT in digestive system diseases.Eur Radiol. 2025 Jun;35(6):3547-3557. doi: 10.1007/s00330-024-11290-6. Epub 2024 Dec 19. Eur Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39699679 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-parametric MRI diffusion models combined with clinical information for predicting Ki-67 expression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: a prospective cohort study.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025 Aug 29. doi: 10.1007/s00261-025-05164-8. Online ahead of print. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025. PMID: 40879693
References
-
- Rahib L, Smith BD, Aizenberg R, Rosenzweig AB, Fleshman JM, Matrisian LM. Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: the unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res. 2014;74:2913–21. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023;73:17–48. - PubMed
-
- Scholzen T, Gerdes J. The Ki-67 protein: from the known and the unknown. J Cell Physiol. 2000;182:311–22. - PubMed
-
- Jamieson NB, Carter CR, McKay CJ, Oien KA. Tissue biomarkers for prognosis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:3316–31. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

