From novice to proficient: a longitudinal study of POCUS skill development through a hybrid certification program in the United Arab Emirates
- PMID: 40247259
- PMCID: PMC12007165
- DOI: 10.1186/s12909-025-07138-2
From novice to proficient: a longitudinal study of POCUS skill development through a hybrid certification program in the United Arab Emirates
Abstract
Background: Point-of-care Ultrasound (POCUS) is rapidly becoming an indispensable tool in a wide range of medical specialties. To ensure that practicing physicians are fully equipped with the skills required, there is a need to expand comprehensive training opportunities, particularly in the Middle East and North Africa region. This study evaluates the effectiveness of a novel year-long hybrid POCUS certification program aimed at enhancing the confidence and competency of practicing physicians in the United Arab Emirates (UAE).
Methods: A prospective cohort study was conducted involving 12 practicing physicians enrolled in a one-year, part-time hybrid POCUS program. The program consisted of six modules that integrated online educational units, in-person workshops, and supervised clinical practice. Eligibility criteria for the program required participants to be licensed physicians with access to an ultrasound machine that had image storage capabilities within their healthcare setting. Participants' confidence was assessed through self-reported surveys at four evaluation points. Competency was evaluated using the Ultrasound Competency Assessment Tool (UCAT) at three evaluation points, while ultrasound image quality was assessed throughout the program. Repeated measures of analysis of variance (ANOVA) were used to analyze changes in confidence and competency over time. Spearman's correlation coefficients were calculated to examine the relationship between confidence and competency scores.
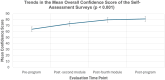
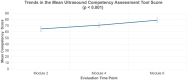
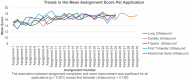
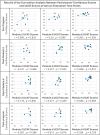
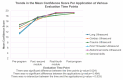
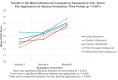
Results: Participants demonstrated significant improvements in both confidence and competency. Mean total confidence scores increased from 64.0 (SD = 9.9) pre-program to 81.3 (SD = 6.7) post-program (p < 0.001). The UCAT scores improved from 64.9 (SD = 13.5) in module two to 78.9 (SD = 3.6) in module six (p < 0.001). The UCAT scores for cardiac and lung applications showed the most consistent improvement, while the scores for first trimester ultrasound demonstrated the least improvement. Ultrasound image quality scores demonstrated a positive trend over time with a clear learning trajectory marked by three distinct phases. There was a significant association between ultrasound image quality scores and the number of completed ultrasound scan assignments (p < 0.001) for all applications except for first trimester ultrasound, indicating the need for curriculum enhancement in this area. A moderate positive correlation was observed between post-module four confidence scores and module six competence scores (r = 0.585, p = 0.059), however, this correlation was not statistically significant.
Conclusion: This comprehensive hybrid POCUS program effectively enhanced confidence and competency among practicing physicians. The structured approach, which integrates theoretical knowledge, hands-on practice, and ongoing longitudinal feedback, presents a promising model for POCUS education. These findings inform the development of similar programs, potentially improving POCUS adoption and patient care globally.
Clinical trial number: Not applicable.
Keywords: Clinical competence; Competency-Based education; Curriculum; Education, medical, continuing; Emergency medicine; Point-of-care ultrasound; Program evaluation; Simulation training; Ultrasonography; United Arab Emirates.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Ethical approval for the study was granted by the Mohammed Bin Rashid University of Medicine and Health Sciences Institutional Review Board (MBRU IRB-2022-172). All methods were performed in accordance with guidelines and regulations on research with human subjects. A written informed consent was obtained from the participants. To protect the anonymity of the participants, each was assigned a unique identifier. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of a novel curriculum on point-of-care ultrasound competency and confidence.Emerg Radiol. 2020 Feb;27(1):37-40. doi: 10.1007/s10140-019-01726-8. Epub 2019 Sep 4. Emerg Radiol. 2020. PMID: 31485848
-
General practitioners' scanning competence following tailored ultrasound training: a hybrid effectiveness-implementation study.BMC Med Educ. 2025 May 20;25(1):733. doi: 10.1186/s12909-025-07356-8. BMC Med Educ. 2025. PMID: 40394656 Free PMC article.
-
The assessment of point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) in residency: the benefits of a four-year longitudinally integrated curriculum.J Osteopath Med. 2025 Jan 8;125(3):119-126. doi: 10.1515/jom-2024-0046. eCollection 2025 Mar 1. J Osteopath Med. 2025. PMID: 39764717
-
Evaluation of Trainee Competency with Point-of-Care Ultrasonography (POCUS): a Conceptual Framework and Review of Existing Assessments.J Gen Intern Med. 2019 Jun;34(6):1025-1031. doi: 10.1007/s11606-019-04945-4. J Gen Intern Med. 2019. PMID: 30924088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Point-of-Care Ultrasound Competency, Credentialing and Policies.Med Clin North Am. 2025 Jan;109(1):285-297. doi: 10.1016/j.mcna.2024.07.001. Epub 2024 Oct 10. Med Clin North Am. 2025. PMID: 39567098 Review.
References
-
- Díaz-Gómez JL, Mayo PH, Koenig SJ. Point-of-Care ultrasonography. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(17):1593–602. - PubMed
-
- IFEM Point-of-Care Ultrasound Curriculum Guidance [Internet]. International Federation for Emergency Medicine. 2014. Available from: https://assets.nationbuilder.com/ifem/pages/126/attachments/original/165... - PubMed
-
- Ultrasound Guidelines. Emergency, Point-of -care, and Clinical Ultrasound Guidelines in Medicine [Internet]. 2023 [cited 2024 Mar 27]. Available from: https://www.acep.org/patient-care/policy-statements/ultrasound-guideline...
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

