Epidemiological characteristics and risk factors for prolonged hospitalisation in oral and maxillofacial space infections: a 3-year retrospective study of 217 cases
- PMID: 40247267
- PMCID: PMC12007366
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-025-05971-x
Epidemiological characteristics and risk factors for prolonged hospitalisation in oral and maxillofacial space infections: a 3-year retrospective study of 217 cases
Abstract
Background: Oral and maxillofacial space infections (OMSIs) are a serious emergency disease in oral and maxillofacial departments; untreated or undertreated OMSI can lead to serious complications and can be life-threatening. This study aimed to comprehensively analyse the epidemiological characteristics of OMSI, identify the associated etiological and risk factors, and develop a machine learning-based predictive model for factors influencing hospitalisation.
Methods: Medical records of 217 patients hospitalised with OMSI were retrospectively analysed. Demographic data, clinical characteristics, treatment histories, microbiological profiles, and drug sensitivity test results were reviewed. A risk prediction model for hospitalisation length was established using machine learning.
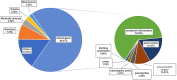
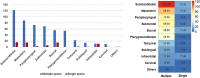
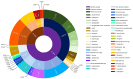
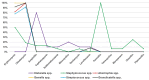
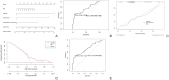
Results: Odontogenic infections (69.41%) were the most common etiological factors for OMSI, with periapical periodontitis being the most prevalent. Streptococcus spp. was the most frequently cultured aerobic bacteria, whereas Peptostreptococcus anaerobius was the predominant anaerobe. Drug sensitivity tests indicated high resistance rates to clindamycin and erythromycin among aerobic bacteria. The risk prediction model exhibited an area under the curve of 0.726 and was validated by an internal area under the curve of 0.712. Factors such as hypertension, diabetes, pre-admission interventions, and age were significantly associated with prolonged hospitalisation.
Conclusion: Periapical periodontitis remains a primary cause of OMSI; however, the rising incidence of infections due to cosmetic injections and implant surgeries warrants attention. Penicillin, clindamycin, and erythromycin are not recommended as empirical first-choice drugs. The predictive model effectively identified risk factors for extended hospitalisation. Hypertension, diabetes, pre-admission interventions, and age are risk factors for lengthened hospitalisation. Efforts should be made to promote oral hygiene education and healthcare system reforms in regions with similar demographic and socioeconomic conditions.
Keywords: Epidemiological; Hospitalisation time; Machine learning; Maxillofacial space infection; Microbiology; Risk factors.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was conducted in accordance with the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Third Affiliated Hospital of Air Force Military Medical University (approval no. KY-OT-20240039). The requirement for informed consent was waived by the Institutional Review Board because of the retrospective nature of the study. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Li YP, Shi B, Zhang JR, Liu YP, Shen GF, Guo CB, Yang C, Li ZB, Zhang ZG, Wang HM, et al. [Expert consensus on the treatment of oral and maxillofacial space infections]. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2021;56(2):136–44. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

