Lactobacillus acidophilus extracellular vesicles-coated UiO-66-NH2@siRNA nanoparticles for ulcerative colitis targeted gene therapy and gut microbiota modulation
- PMID: 40247297
- PMCID: PMC12007195
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-025-03376-0
Lactobacillus acidophilus extracellular vesicles-coated UiO-66-NH2@siRNA nanoparticles for ulcerative colitis targeted gene therapy and gut microbiota modulation
Erratum in
-
Correction: Lactobacillus acidophilus extracellular vesiclescoated UiO-66-NH2@siRNA nanoparticles for ulcerative colitis targeted gene therapy and gut microbiota modulation.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 May 13;23(1):341. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03413-y. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40355904 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
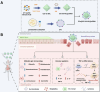
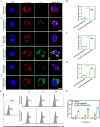
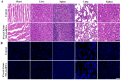
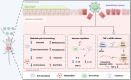
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a complex and chronic inflammatory bowel disease whose pathogenesis involves genetic and environmental factors, which poses a challenge for treatment. Here, we have designed an innovative integrated therapeutic strategy using Lactobacillus acidophilus extracellular vesicles (EVs) to encapsulate UiO-66-NH2 nanoparticles bounded with TNF-α siRNA (EVs@UiO-66-NH2@siRNA) for UC treatment. This system shows superior affinity to inflammation-related cells due to the Lactobacillus acidophilus EVs can maintain immune homeostasis by regulating the secretion of cytokines in vitro. siRNA can specifically target the key inflammatory TNF-α in UC and silence its gene expression, thereby regulating the process of inflammatory response. After oral administration, EVs@UiO-66-NH2@siRNA demonstrates an accurate delivery of TNF-α siRNA to colonize the colon site and exerts a siRNA therapeutic effect by inhibiting the expression of TNF-α, which alleviates the intestinal inflammation in DSS-induced UC model. Moreover, this system can modulate the types and compositional structures of gut microbiota and metabolites to achieve an anti-inflammatory phenotype, which is helpful for the repair of intestinal homeostasis. We also have proved that UiO-66-NH2 nanoparticles exhibit a high loading capacity for TNF-α siRNA and good pH responsiveness, improving the potent release of siRNA in colon tissue. Collectively, the EVs@UiO-66-NH2@siRNA nano-delivery system demonstrate a feasible combination therapeutic strategy for UC through gut microecology modulation, immune regulation and TNF-α siRNA silence, which may provide a potential targeted treatment approach for inflammatory bowel disease.
Keywords: Lactobacillus acidophilus EVs; TNF-α SiRNA; Targeted gene therapy; UiO-66-NH2; Ulcerative colitis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All animal experiments were conducted under the Regional Ethics Committee for Animal Experiments at Zhengzhou University. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Gros B, Kaplan GG. Ulcerative colitis in adults: A review. JAMA. 2023;330:951–65. - PubMed
-
- Adams A, Gupta V, Mohsen W, Chapman TP, Subhaharan D, Kakkadasam Ramaswamy P, Kumar S, Kedia S, McGregor CG, Ambrose T, et al. Early management of acute severe UC in the biologics era: development and international validation of a prognostic clinical index to predict steroid response. Gut. 2023;72:433–42. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

