A nerve root decompression position identified by 3D CT scan: the modified reversed contralateral axial rotation position for patients with lumbar disc prolapse
- PMID: 40247336
- PMCID: PMC12007341
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-025-05762-8
A nerve root decompression position identified by 3D CT scan: the modified reversed contralateral axial rotation position for patients with lumbar disc prolapse
Abstract
Background: Nerve root compression in the lumbar intervertebral foramen (LIVF) is a consistent feature of radicular syndrome. There is debate about movements and positions that may reduce compression for possible use in conservative treatment.
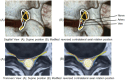
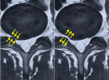
Purpose: To investigate real-time effects of specific 3 dimensional positioning of the trunk on the cross sectional area (CSA) of the LIVF in patients with lumbar disc prolapse and radiculopathy using 3D-CT scan imaging.
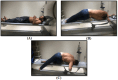
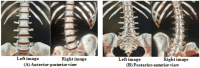
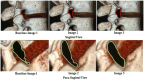
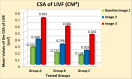
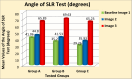
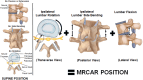
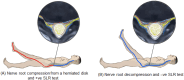
Methods: Ninety males aged between 20 and 40 years with unilateral lumbar disc prolapse and radiculopathy were separated into three equal groups based on the level of disc prolapse. Group (A): L3/L4, group (B): L4/L5, and group (C): L5/S1. All underwent three separate imaging sessions; first in the supine position to establish baseline data (Baseline-Image 1), followed by a modified reversed contralateral axial rotation position (Image 2), and finally the same position as Image 2 but after 48 h of using the position as a therapeutic intervention (Image 3). The CSA of LIVF at L3/L4, L4/L5, and L5/S1 levels and the angles of straight leg raising (SLR) test were measured following each imaging session.
Results: Two-way mixed MANOVA analysis revealed that the mean values of the CSA of LIVF and the angle of SLR test were significantly increased in Image 2 compared with Baseline-Image 1 across all tested groups (P = 0.001). Moreover, the measured outcome variables were significantly increased in Image 3 compared with Image 2 and Baseline-Image 1 across all tested groups (P = 0.001).
Conclusion: The modified reversed contralateral axial rotation position of the trunk had a real-time decompression effect on the impinged nerve roots in patients with unilateral lumbar disc prolapse and radiculopathy.
Keywords: Lumbar disc prolapse; Lumbar intervertebral foramen; Modified reversed contralateral axial rotation position; Nerve root decompression position; Radiculopathy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- El-shetry E, Elwan N, Mohamad H, Elsayed M, Ibrahim A. Lower three lumbar intervertebral foramina measurements of adult Egyptians in relation to age and sex using magnetic resonance imaging. Zagazig Univ Med J. 2023;29(2):690–6.
-
- Dydyk AM, Ngnitewe Massa R, Mesfin FB. Disc Herniation. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Puplishing; 2024; Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441822/ - PubMed
-
- Fujiwara A, An HS, Lim TH, Haughton VM. Morphologic changes in the lumbar intervertebral foramen due to Flexion-Extension, lateral bending, and axial rotation: an in vitro anatomic and Biomechanical study. Spine. 2001;26(8):876–82. - PubMed
-
- Mitchell UH, Wooden MJ, McKeough DM. The Short-Term effect of lumbar positional distraction. J Man Manipulative Therapy. 2001;9(4):213–21.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

