Mammalian Ste20-like kinase 1 regulates AMPK to mitigate the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- PMID: 40247356
- PMCID: PMC12004885
- DOI: 10.1186/s40001-025-02557-9
Mammalian Ste20-like kinase 1 regulates AMPK to mitigate the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Abstract
Background: Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) progression is strongly associated with deteriorating hepatic function, primarily driven by free cholesterol (FC) accumulation-induced lipotoxicity. Emerging evidence highlights the regulatory role of mammalian Ste20-like kinase 1 (MST1) in modulating intrahepatic lipid homeostasis, suggesting its therapeutic potential for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) management. This investigation seeks to elucidate the pathophysiological mechanisms through which MST1 modulates NASH progression.
Methods: The experimental design employed two murine genetic models-wild-type (WT) controls and MST1-knockout (MST1-KO) specimens-subjected to a nutritionally modified Western diet (WD) enriched with saturated fats, simple carbohydrates, and dietary cholesterol to induce non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) pathogenesis. Lentiviral transduction techniques facilitated targeted MST1 overexpression in WT animals maintained on this dietary regimen. Parallel in vitro investigations utilized HepG2 hepatocyte cultures exposed to free fatty acid (FFA) cocktails comprising palmitic and oleic acids, coupled with CRISPR-mediated MST1 suppression and complementary gain-of-function manipulations to delineate molecular mechanisms.
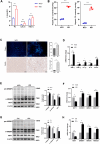
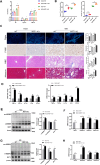
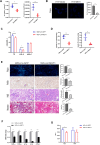
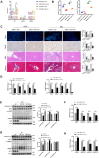
Results: NASH triggers hepatic sterol biosynthesis activation, resulting in pathological FC overload concurrent with MST1 transcriptional suppression. Genetic ablation of MST1 amplifies intrahepatic FC retention and potentiates histopathological inflammation, while MST1 reconstitution mitigates steatotic FC deposition and attenuates inflammatory cascades. Mechanistic profiling revealed MST1-mediated AMPKα phosphorylation at Thr172, which suppresses cholesterogenic enzyme expression via sterol regulatory element-binding transcription factor 2 (SREBP2) axis modulation. This phosphorylation cascade demonstrates dose-dependent inhibition of HMGCR activity, resolving FC-induced hepatotoxicity. Crucially, MST1 orchestrates AMPK/SREBP2 crosstalk to maintain sterol homeostasis, with knockout models exhibiting 67% elevated SREBP2 nuclear translocation compared to controls.
Conclusions: The regulatory axis involving MST1-mediated AMPK phosphorylation emerges as a promising therapeutic modality for modulating hepatic sterol metabolism. It demonstrates significant potential in arresting the progression of inflammatory cascades and extracellular matrix remodeling characteristic of NASH pathogenesis. Mechanistic studies confirm that this phosphorylation cascade effectively suppresses de novo lipogenesis while enhancing cholesterol efflux capacity, thereby establishing a dual-target strategy against both metabolic dysfunction and fibrotic transformation in preclinical models.
Keywords: AMP-activated protein kinase; Cholesterol synthesis; Hepatic free cholesterol; Mammalian sterile 20-like kinase 1; Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study strictly followed the Guidelines for the Care and Use of Experimental Animals published by the National Institutes of Health, and all experimental protocols were approved by the Medical Ethics Review Committee of Ningxia Medical University (IACUC- 2023 - 001). Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mechanism of protecting hepatocytes in NAFLD through MST1-FOXO3a-SREBP2 pathway.Endokrynol Pol. 2025;76(3):265-278. doi: 10.5603/ep.103350. Endokrynol Pol. 2025. PMID: 40586403
-
Suppression of insulin-induced gene 1 (INSIG1) function promotes hepatic lipid remodelling and restrains NASH progression.Mol Metab. 2021 Jun;48:101210. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2021.101210. Epub 2021 Mar 17. Mol Metab. 2021. PMID: 33722690 Free PMC article.
-
Gracilaria chorda subcritical water ameliorates hepatic lipid accumulation and regulates glucose homeostasis in a hepatic steatosis cell model and obese C57BL/6J mice.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Feb 10;320:117395. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.117395. Epub 2023 Nov 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37952731
-
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;960:443-467. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-48382-5_19. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28585211 Review.
-
The ménage à trois of autophagy, lipid droplets and liver disease.Autophagy. 2022 Jan;18(1):50-72. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2021.1895658. Epub 2021 Apr 2. Autophagy. 2022. PMID: 33794741 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Younossi ZM, Koenig AB, Abdelatif D, Fazel Y, Henry L, Wymer M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease—Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology. 2016;64:73–84. 10.1002/hep.28431. - PubMed
-
- Karim G, Department of Medicine, Mount Sinai Israel, New York, NY, USA, Bansal MB, Division of Liver Diseases, Department of Medicine, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, USA. Resmetirom: an orally administered, small-molecule, liver-directed, β-selective THR agonist for the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Eur Endocrinol. 2023;19:60. 10.17925/EE.2023.19.1.60
-
- Fiorucci S, Biagioli M, Sepe V, Zampella A, Distrutti E. Bile acid modulators for the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2020;29:623–32. 10.1080/13543784.2020.1763302. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

