Transgenically expressed human delta epithelial sodium channel facilitated fluid absorption in mouse fetal lung explants
- PMID: 40247623
- PMCID: PMC12124468
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00028.2025
Transgenically expressed human delta epithelial sodium channel facilitated fluid absorption in mouse fetal lung explants
Abstract
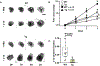
Epithelial sodium channels (ENaCs) are essential for sodium (Na+) transport and maintaining fluid balance, which is vital for the removal of fetal fluid at birth and the homeostasis of luminal fluid in the lungs. In mice, ENaC is composed of three subunits (α, β, and γ). However, in humans, a fourth δ-subunit is also expressed. This study investigated the physiological role of the δ-ENaC in fetal/neonatal lungs, an area that remains less explored despite its potential significance. We measured expansion in mouse E15 lung explants expressing human δ-ENaC (SCNN1D-Tg). We found that transgenic expression of δ-ENaC enhanced fluid absorption and significantly reduced the surface area increase compared with wild-type (WT) explants (142.30 ± 5.81% vs. 163.80 ± 5.95% expansion, P < 0.001). Amiloride treatments revealed that both α-ENaC and δ-ENaC contributed to fluid absorption. No statistical significance was observed in the amiloride-sensitive fraction of SCNN1D-Tg explants compared with WT preparations in the presence of 100 µM amiloride (P = 0.400). In contrast, a significant reduction in amiloride-sensitive fraction in SCNN1D-Tg explants was observed in the presence of 10 µM amiloride (P < 0.001). Furthermore, specific blocking of α-ENaC using α-13 inhibitory peptide resulted in a 2.12-fold growth increase in WT explants, compared with a 1.47-fold increase in SCNN1D-Tg explants (P < 0.001). In summary, this study provides evidence that δ-ENaC may contribute to fluid absorption in E15 and newborn lungs, highlighting its significance in alveolar fluid regulation in prenatal and postnatal lungs.NEW & NOTEWORTHY The findings of our study highlight the significance of δ-ENaC in lung fluid regulation. Transgenic expression of human δ-ENaC contributes to fluid absorption increase, supporting its potential as a pathway for alveolar fluid clearance in E15 and postnatal lungs.
Keywords: E15 lung explants; amiloride; epithelial sodium channels; lung explants; α-13 peptide.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURES:
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Elias N, Rafii B, Rahman M, Otulakowski G, Cutz E, and O’Brodovich H. The role of alpha-, beta-, and gamma-ENaC subunits in distal lung epithelial fluid absorption induced by pulmonary edema fluid. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 293: L537–545, 2007. - PubMed
-
- Hummler E, Barker P, Gatzy J, Beermann F, Verdumo C, Schmidt A, Boucher R, and Rossier BC. Early death due to defective neonatal lung liquid clearance in alpha-ENaC-deficient mice. Nat Genet 12: 325–328, 1996. - PubMed
-
- Waldmann R, Champigny G, Bassilana F, Voilley N, and Lazdunski M. Molecular cloning and functional expression of a novel amiloride-sensitive Na+ channel. J Biol Chem 270: 27411–27414, 1995. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

