GOT2: New therapeutic target in pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 40247913
- PMCID: PMC12005923
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gendis.2024.101370
GOT2: New therapeutic target in pancreatic cancer
Abstract
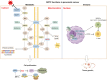
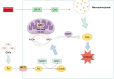
In recent years, the incidence and mortality rates of pancreatic cancer have been steadily increasing, and conventional therapies have shown a high degree of tolerance. Therefore, the search for new therapeutic targets remains a key issue in current research. Mitochondrial glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase 2 (GOT2) is an important component of the malate-aspartate shuttle system, which plays an important role in the maintenance of cellular redox balance and amino acid metabolism, and has the potential to become a promising target for anti-cancer therapy. In this paper, we will elaborate on the metabolic and immune effects of GOT2 in pancreatic cancer based on existing studies, with a view to opening up new avenues for the treatment of pancreatic cancer.
Keywords: GOT2; Glutamine metabolism; PPARδ; Pancreatic cancer; Tumor microenvironment.
© 2024 The Authors. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of KeAi Communications Co., Ltdé.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Rahib L., Smith B.D., Aizenberg R., Rosenzweig A.B., Fleshman J.M., Matrisian L.M. Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030:the unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res. 2014;74(11):2913–2921. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

