Sarcopenia in Peritoneal Dialysis: Prevalence, Pathophysiology, and Management Strategies
- PMID: 40247955
- PMCID: PMC12005912
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xkme.2025.100989
Sarcopenia in Peritoneal Dialysis: Prevalence, Pathophysiology, and Management Strategies
Abstract
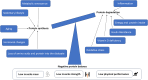
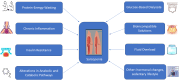
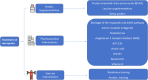
Sarcopenia, defined as the loss of skeletal muscle mass, strength, and function, is a significant complication in patients with chronic kidney disease, particularly those undergoing peritoneal dialysis (PD). This review explores the prevalence, pathophysiology, diagnostic challenges, and management strategies of sarcopenia in the PD population. The multifactorial etiology of sarcopenia in PD, including protein-energy wasting, chronic inflammation, insulin resistance, and hormonal imbalances, underscores the complexity of its management. The prevalence of sarcopenia in patients treated with PD is influenced by age, duration of dialysis, and comorbid conditions, presenting a considerable variation across studies due to differing diagnostic criteria. Diagnostic challenges arise from fluid overload and the PD process, affecting the accuracy of muscle mass measurements. Intervention strategies focusing on nutritional supplementation and physical exercise have shown promise; however, the need for PD-specific diagnostic criteria and treatment protocols remains. This review highlights the critical effect of sarcopenia on functional status and survival in patients treated with PD, emphasizing the importance of addressing this condition to improve patient outcomes. Future directions call for comprehensive, longitudinal studies to better understand sarcopenia's progression in patients treated with PD and the development of tailored interventions.
Keywords: Sarcopenia; dialysis; muscle mass; peritoneal dialysis; protein-energy wasting; treatment.
© 2025 The Authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sarcopenia and Cardiogeriatrics: The Links Between Skeletal Muscle Decline and Cardiovascular Aging.Nutrients. 2025 Jan 14;17(2):282. doi: 10.3390/nu17020282. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 39861412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive Insights into Sarcopenia in Dialysis Patients: Mechanisms, Assessment, and Therapeutic Approaches.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Mar 4;61(3):449. doi: 10.3390/medicina61030449. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40142260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differences in Prevalence of Muscle Wasting in Patients Receiving Peritoneal Dialysis per Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry Due to Variation in Guideline Definitions of Sarcopenia.Nutr Clin Pract. 2017 Aug;32(4):539-544. doi: 10.1177/0884533617696331. Epub 2017 Mar 16. Nutr Clin Pract. 2017. PMID: 28760111
-
Differences in the prevalence of sarcopenia in peritoneal dialysis patients using hand grip strength and appendicular lean mass: depends upon guideline definitions.Eur J Clin Nutr. 2018 Jul;72(7):993-999. doi: 10.1038/s41430-018-0238-3. Epub 2018 Jun 19. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2018. PMID: 29921962
-
Sarcopenia in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Narrative Review from Pathophysiology to Therapeutic Approaches.Biomedicines. 2025 Feb 4;13(2):352. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13020352. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40002765 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Morphofunctional Assessment of Malnutrition and Sarcopenia Using Nutritional Ultrasonography in Patients Undergoing Maintenance Hemodialysis.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Jun 5;61(6):1044. doi: 10.3390/medicina61061044. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40572732 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Sarcopenia Definitions-Variability in Prevalence and Disability Associations in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2025 Aug;16(4):e70018. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.70018. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2025. PMID: 40726317 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous