Predictive value of HBeAg titer dynamics for HBsAg clearance in pediatric chronic hepatitis B
- PMID: 40248021
- PMCID: PMC12003423
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2025.1539300
Predictive value of HBeAg titer dynamics for HBsAg clearance in pediatric chronic hepatitis B
Abstract
Introduction: Achieving functional cure of chronic hepatitis B (CHB), characterized by the loss of HBV DNA and HBsAg, remains challenging in adults but demonstrates higher success rates in children. Elucidating the factors influencing HBsAg loss in pediatric patients is crucial for optimizing treatment strategies. This study aimed to evaluate the predictive value of HBeAg titer dynamics for HBsAg clearance in pediatric CHB and develop a predictive model incorporating these dynamics.
Material and methods: This retrospective cohort study analyzed 119 children aged 1-18 years with CHB treated with nucleos(t)ide analogues. Patient outcomes were evaluated using two independent classification approaches: HBsAg loss status and age stratification (≤6 vs. >6 years). Treatment response was assessed through longitudinal HBeAg titer measurements during the first 12 months. Based on identified predictors, a logistic regression model was developed incorporating age and HBeAg titer dynamics to predict HBsAg clearance probability.
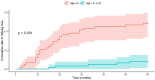
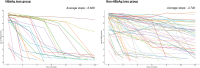
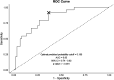
Results: The study population exhibited a median age of 6.2 years. Factors associated with HBsAg loss encompassed younger age, female sex, and absence of breakthrough. In multivariate analysis, younger age was identified as the only significant factor. The cumulative HBsAg loss rate demonstrated markedly higher values in the ≤6 years group (Hazard ratio 7.69). HBeAg titer decline exhibited significantly steeper trajectories in the HBsAg loss group. The developed predictive model, "Log Odds = -1.182 + 0.308 × log_reduction-0.205 × age", demonstrated good performance with high accuracy.
Conclusions: Early HBeAg titer dynamics combined with age at treatment initiation may serve as useful predictors of HBsAg clearance in pediatric CHB. Our predictive model, utilizing readily available semi-quantitative HBeAg measurements, could potentially assist clinicians in therapeutic decision-making and individualized treatment strategies.
Keywords: antiviral agents; children; hepatitis B e antigens; hepatitis B surface antigens; seroconversion.
© 2025 Hong, Hwang, Kim, Do, Kwak, Suh, Choi, Kang and Choe.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Functional cure is associated with younger age in children undergoing antiviral treatment for active chronic hepatitis B.Hepatol Int. 2024 Apr;18(2):435-448. doi: 10.1007/s12072-023-10631-9. Epub 2024 Feb 20. Hepatol Int. 2024. PMID: 38376650 Free PMC article.
-
Early Serum HBsAg Drop Is a Strong Predictor of HBeAg Seroconversion and HBsAg Loss to Pegylated Interferon Alfa-2a in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients with Prior Nucleos(t)ide Analogue Exposure.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Jun 23;25:4665-4674. doi: 10.12659/MSM.916441. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 31230063 Free PMC article.
-
HBsAg and HBcrAg as predictors of HBeAg seroconversion in HBeAg-positive patients treated with nucleos(t)ide analogues.J Viral Hepat. 2018 Aug;25(8):886-893. doi: 10.1111/jvh.12889. Epub 2018 Apr 2. J Viral Hepat. 2018. PMID: 29532589
-
Clinical utility of quantitative HBsAg in natural history and nucleos(t)ide analogue treatment of chronic hepatitis B: new trick of old dog.J Gastroenterol. 2013 Jan;48(1):13-21. doi: 10.1007/s00535-012-0668-y. Epub 2012 Oct 24. J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23090000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A critique and systematic review of the clinical utility of hepatitis B core-related antigen.J Hepatol. 2023 Apr;78(4):731-741. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.12.017. Epub 2022 Dec 28. J Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 36586590
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

