Engineered nanoparticles for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 40248097
- PMCID: PMC12003369
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1510798
Engineered nanoparticles for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
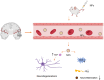
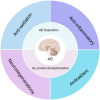
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is one of the most common diseases characterized by neurodegeneration and is becoming a major public health problem worldwide. AD is manifested mainly by progressive impairments in cognition, emotion, language and memory in the elderly population. Many treatment strategies have been explored for decades; however, there is still no effective way to address the root cause of AD pathogenesis, only to target symptoms to improve patient cognitive outcomes. Intracerebral administration is difficult because of the challenges posed by the blood‒brain barrier (BBB). NPs are materials with sizes between 1 and 100 nm that can improve biocompatibility, extend the half-life, transport macromolecules, be delivered across the BBB to the central nervous system, and exhibit good targeting capabilities. NPs can provide new ideas for the treatment of AD in terms of their antiaging, antineuroinflammatory, antioxidative, and nerve repair-promoting effects. In this manuscript, we first describe the relationship between AD and the BBB. Second, we introduce the application of nanoparticles for AD treatment. Finally, we summarize the challenges faced by nanoparticles in the treatment of AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; blood-brain barrier; nanoparticles; nerve regeneration; β amyloid.
Copyright © 2025 Jia, Zhao, Zhao and Gao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Applications of Nanoparticles in Alzheimer's Disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2023;96(2):459-471. doi: 10.3233/JAD-230098. J Alzheimers Dis. 2023. PMID: 37807779 Review.
-
Sialic acid (SA)-modified selenium nanoparticles coated with a high blood-brain barrier permeability peptide-B6 peptide for potential use in Alzheimer's disease.Acta Biomater. 2015 Oct;25:172-83. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2015.06.035. Epub 2015 Jul 2. Acta Biomater. 2015. PMID: 26143603
-
Glucose-modified BSA/procyanidin C1 NPs penetrate the blood-brain barrier and alleviate neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease models.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 May;268(Pt 1):131739. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.131739. Epub 2024 Apr 22. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38657920
-
Neuronal mitochondria-targeted delivery of curcumin by biomimetic engineered nanosystems in Alzheimer's disease mice.Acta Biomater. 2020 May;108:285-299. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.03.029. Epub 2020 Apr 3. Acta Biomater. 2020. PMID: 32251785
-
Recent Advances in the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease Using Nanoparticle-Based Drug Delivery Systems.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Apr 11;14(4):835. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14040835. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35456671 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pathological mechanisms and treatment progression of Alzheimer's disease.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Jul 14;30(1):625. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02886-9. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40660381 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Brain-Targeting Nanoparticle Loaded with Biatractylolide and Its Protective Effect on Alzheimer's Disease.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 May 28;18(6):809. doi: 10.3390/ph18060809. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40573206 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abd Elmonem H. A., Morsi R. M., Mansour D. S., El-Sayed E. R. (2023). Myco-fabricated ZnO nanoparticles ameliorate neurotoxicity in mice model of Alzheimer’s disease via acetylcholinesterase inhibition and oxidative stress reduction. Biometals 36, 1391–1404. 10.1007/s10534-023-00525-6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

