Early Intervention with Mepolizumab, Corticosteroids, and Intravenous Immunoglobulin for Dupilumab-Triggered Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis: A Case Report
- PMID: 40248105
- PMCID: PMC12005197
- DOI: 10.2147/JAA.S513640
Early Intervention with Mepolizumab, Corticosteroids, and Intravenous Immunoglobulin for Dupilumab-Triggered Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis: A Case Report
Abstract
Introduction: Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA) is a rare complication during dupilumab therapy. However, the optimal treatment strategy for dupilumab-triggered EGPA remains unclear, particularly the timing and role of anti-interleukin-5 therapy.
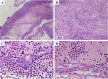
Case study: A 48-year-old female with severe eosinophilic rhinosinusitis and asthma, increased blood eosinophils (2098/μL) and myeloperoxidase-specific antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (MPO-ANCA) (46.1 U/mL) without vasculitic symptoms, developed systemic symptoms, including fever, arthralgia, and peripheral neuropathy immediately after dupilumab administration.
Results: Physical assessment revealed bilateral expiratory wheezes and laboratory tests revealed marked elevations in blood eosinophil (11,889/μL) and MPO-ANCA levels (125.0 U/mL). Other conditions, including parasitic infections, allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, and FIP1L1-PDGFRA-positive disease, were excluded. Early intervention with mepolizumab (300 mg), methylprednisolone pulse therapy, and intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) was initiated after discontinuing dupilumab, resulting in rapid normalization of blood eosinophil counts and clinical improvement. Residual neuropathy was successfully treated with intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg). Prednisolone was reduced to 15 mg daily with negative MPO-ANCA one month after treatment initiation.
Conclusion: This case emphasizes the importance of monitoring preexisting MPO-ANCA and blood eosinophils before and during dupilumab therapy. Early intervention with mepolizumab combined with conventional therapy is considered an optimal treatment strategy for dupilumab-triggered EGPA.
Keywords: Churg-Strauss syndrome; antibodies; antineutrophil; cytoplasmic; dupilumab; eosinophils; mepolizumab.
© 2025 Kaburaki et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Masahiro Seike reports grants and/or personal fees from AstraZeneca, Chugai Pharmaceutical, MSD K.K, Taiho Pharmaceutical, Eli Lilly, Ono Pharmaceutical, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim, Pfizer, Novartis, Takeda Pharmaceutical, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Nippon Kayaku, Daiichi-Sankyo Company, Merck Biopharma, and Amgen Inc, outside the submitted work. The authors report there are no other competing interests to declare in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MPO-ANCA-positive eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis complicated by alveolar haemorrhage treated with mepolizumab as an induction therapy: Case report.Mod Rheumatol Case Rep. 2025 Jul 25;9(2):rxae088. doi: 10.1093/mrcr/rxae088. Mod Rheumatol Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 39707621
-
Dupilumab-induced Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis Complicated by Peripheral Neuropathic Pain: a Case Report and Literature Review.J Clin Immunol. 2025 Jul 24;45(1):114. doi: 10.1007/s10875-025-01914-x. J Clin Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40705100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two unique cases of eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis in childhood treated with anti-interleukin-5 therapy: infantile-onset and submandibular salivary gland involvement.Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2025 Jun 2;23(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s12969-025-01115-1. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2025. PMID: 40457436 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical value of biomarkers in relation to artery size in eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis: findings from an inception cohort at a Japanese City Hospital.Clin Rheumatol. 2025 Aug 18. doi: 10.1007/s10067-025-07634-2. Online ahead of print. Clin Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40824340
-
Anti-IL5 therapies for asthma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Sep 21;9(9):CD010834. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010834.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 12;7:CD010834. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010834.pub4. PMID: 28933516 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Antonelou M, Perea Ortega L, Harvey J, Salama AD. Anti-myeloperoxidase antibody positivity in patients without primary systemic vasculitis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2019;37(Suppl 117):86–89. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

