Development and validation of a recombinant human TNF-α based ELISA to detect and quantify adalimumab
- PMID: 40248135
- PMCID: PMC12005340
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2025.102005
Development and validation of a recombinant human TNF-α based ELISA to detect and quantify adalimumab
Abstract
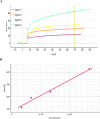
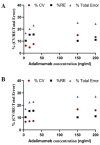
Adalimumab, a humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody is currently used to treat inflammatory diseases. However, a sensitive, in-house ELISA for evaluating inter- and intra-individual pharmacokinetic variability of adalimumab remains limited. In this study, an ELISA was developed to measure adalimumab levels, using recombinant human TNF-α (rhTNF-α) as capture antibody. Initially, surface plasma resonance showed acceptable binding kinetics (KD) of 2.38x10-07 nM for adalimumab. Next, a standard curve of adalimumab (1.54 ng/ml to 300 ng/ml), with five quality control points (5.2, 16, 27, 150, and 200 ng/ml) was evaluated for inter and intra-assay accuracy and precision, using serum matrix, by four independent validations. The linear range of the validated assay was 5.2 ng/ml to 200 ng/ml, upper limit of quantification (ULOQ) and lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) were 200 ng/ml and 5.2 ng/ml, respectively. The assay specificity was validated by testing cross-reactivity of rituximab with rhTNF-α, which was found to be non-reactive. Further, the hook effect was over-ruled by diluting the highest concentration of adalimumab tested to assay linear range, and dilution integrity was observed for entire concentrations within linear range (%RE ≤ 20 %), as recommended by European Medicines Agency. Collectively, this rhTNF-α binding-based ELISA method is highly sensitive, reproducible, and useful for monitoring adalimumab.
Keywords: Adalimumab; Arthritis; Bioanalysis; ELISA; Inflammation; Pharmacokinetics; TNF-Alpha.
© 2025 Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
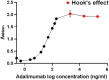
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. Dilution linearity exhibited the hook effect over and above the assay linear range. The adalimumab was prepared at 1000X of 1000 ng/ml and diluted 10 times to the concentration within the assay range, using an assay diluent. Different concentrations of adalimumab were prepared and the hook effect in the assay was determined. The Hook's effect was observed beyond the linear range of the assay, and the non-linearity was observed beyond the detection range.
Figures




References
-
- Jedli O., et al. Attenuation of ovalbumin-induced inflammation and lung oxidative injury in asthmatic rats by Zingiber officinale extract: combined in silico and in vivo study on antioxidant potential, STAT6 and TNF-α pathways. 3 Biotech. 2022;12(9):191. doi: 10.1007/s13205-022-03249-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

