TAp73 modulates proliferation and ferroptosis in mammary epithelial cells
- PMID: 40248352
- PMCID: PMC12003338
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1532910
TAp73 modulates proliferation and ferroptosis in mammary epithelial cells
Abstract
Introduction: TAp73, a transcriptionally active isoform of the p73 gene, is essential for epithelial tissue development. Ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death characterized by lipid peroxidation and reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation, has been increasingly studied in recent years. However, its role in epithelial cells and the regulatory function of TAp73 in this context remain poorly understood.
Methods: We investigated the role of TAp73 in epithelial cell proliferation and ferroptosis using ectopic overexpression and RNA interference approaches. Cell proliferation was assessed through colony formation and DNA synthesis assays. Ferroptosis was induced using RSL3, and the effects were evaluated by measuring cell viability, ROS levels, and the expression of ferroptosis-associated genes PTGS2 and TFRC.
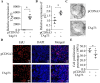
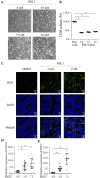
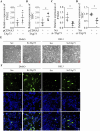
Results: TAp73 overexpression significantly increased p21 expression, suppressed colony formation and DNA synthesis, thereby inhibiting cell proliferation. In contrast, TAp73 knockdown reduced p21 levels and enhanced cell proliferation. RSL3 treatment induced a dose-dependent increase in cell death and ROS accumulation, confirming the susceptibility of epithelial cells to ferroptosis. Furthermore, TAp73 overexpression enhanced RSL3-induced ferroptosis by upregulating PTGS2 and TFRC, while TAp73 knockdown diminished their expression, reducing oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation.
Conclusion: TAp73 acts as a dual regulator of epithelial cell fate by inhibiting proliferation and promoting ferroptosis. These findings reveal a novel role for TAp73 in epithelial cell biology and suggest potential therapeutic targets for diseases involving epithelial cell death.
Keywords: TAp73; cell death; ferroptosis; mammary epithelial cells; proliferation.
Copyright © 2025 Sun, Ren, Chen, Zhang, Mei, Wen, Zhang, Li, Yan and Lai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

