Phospholipid scramblase 1: a frontline defense against viral infections
- PMID: 40248364
- PMCID: PMC12003403
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1573373
Phospholipid scramblase 1: a frontline defense against viral infections
Abstract
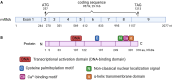
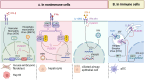
Phospholipid scramblase 1 (PLSCR1) is the most studied member of the phospholipid scramblase protein family. Its main function is to catalyze calcium (Ca2+)-dependent, ATP-independent, bidirectional and non-specific translocation of phospholipids between inner and outer leaflets of plasma membrane. Additionally, PLSCR1 is identified as an interferon-stimulated gene (ISG) with antiviral activities, and its expression can be highly induced by all types of interferons in various viral infections. Indeed, numerous studies have reported the direct antiviral activities of PLSCR1 through interrupting the replication processes of a variety of viruses, including entry of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), nuclear localization of influenza A virus (IAV), and transactivation of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), human T-cell leukemia virus type-1 (HTLV1), human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) and hepatitis B virus (HBV). In addition to these direct antiviral activities, PLSCR1 also regulates endogenous immune components to defend against viruses in both nonimmune and immune cells. Such activities include potentiation of ISG transcription, activation of JAK/STAT pathway, upregulation of type 3 interferon receptor (IFN-λR1) and recruitment of Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9). This review aims to summarize the current understanding of PLSCR1's multiple roles as a frontline defense against viral infections.
Keywords: Epstein-Barr virus; HBV - hepatitis B virus; HCMV (human cytomegalovirus); HIV; PLSCR1; SARS-CoV-2; antiviral; influenza A virus.
Copyright © 2025 Yang, Norbrun, Sorkhdini and Zhou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

