Multiple routes for non-physiological l-threonine uptake in Escherichia coli K-12
- PMID: 40248429
- PMCID: PMC12003319
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1579813
Multiple routes for non-physiological l-threonine uptake in Escherichia coli K-12
Abstract
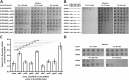
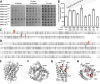
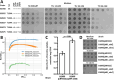
In this study, we identified eight multicopy suppressors (yhjE, sdaC, ydgI, alaE, ychE, yqeG, proP, and yjeM) and three distinct classes of chromosomal mutations (lrp, marC, and cycA) capable of complementing the growth defect caused by threonine uptake deficiency in the sstT tdcC livKHMGF brnQ thrP strain. YhjE, SdaC, YdgI, AlaE, mutant MarC, and CycA exhibited measurable threonine-specific uptake activity in the in vitro assay. Phenotypic assays revealed that YhjE and SdaC were the main entry points for threonine in a strain lacking major threonine-specific permeases. A derivative of the threonine-auxotrophic sstT tdcC livKHMGF brnQ thrP mutant, harboring deletions of eight multicopy suppressors, exhibited significantly reduced fitness at subsaturating threonine concentrations and improved fitness at toxic threonine concentrations, indicating a defect in membrane permeability. These results may help guide the effective construction of threonine-producing strains, extend knowledge on the substrate preferences of SdaC, AlaE, and ProP, and provide clues for further studies on the exact substrate range of YhjE, YdgI, YjeM, YchE, MarC, and YqeG whose physiologically relevant functions have not yet been established.
Keywords: Escherichia coli; amino acid transporter; l-threonine uptake; membrane proteins; transmembrane transport.
Copyright © 2025 Bubnov, Khozov, Vybornaya, Stepanova, Molev, Melkina, Badun, Chernysheva, Skob, Netrusov and Sineoky.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A study on L-threonine and L-serine uptake in Escherichia coli K-12.Front Microbiol. 2023 Mar 21;14:1151716. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1151716. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37025642 Free PMC article.
-
Improving L-serine formation by Escherichia coli by reduced uptake of produced L-serine.Microb Cell Fact. 2020 Mar 14;19(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s12934-020-01323-2. Microb Cell Fact. 2020. PMID: 32169078 Free PMC article.
-
A novel membrane-associated threonine permease encoded by the tdcC gene of Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4288-94. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4288-4294.1990. J Bacteriol. 1990. PMID: 2115866 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli and Corynebacterium glutamicum for the production of L-threonine.Biotechnol Adv. 2011 Jan-Feb;29(1):11-23. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2010.07.009. Epub 2010 Aug 3. Biotechnol Adv. 2011. PMID: 20688145 Review.
-
First aid interventions by laypeople for acute oral poisoning.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Dec 19;12(12):CD013230. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013230. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30565220 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

