[Malaria control in French Guiana: What are the challenges in this last endemic French territory in 2024?]
- PMID: 40248577
- PMCID: PMC12001996
- DOI: 10.48327/mtsi.v5i1.2025.536
[Malaria control in French Guiana: What are the challenges in this last endemic French territory in 2024?]
Abstract
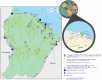
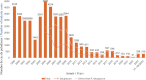
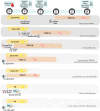
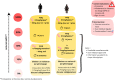
French Guiana, the last malaria-endemic region of France, is facing an epidemic resurgence of malaria since the end of 2023. This epidemic, primarily caused by Plasmodium vivax, mainly affects populations that are far from the healthcare system. It has highlighted the difficulties of providing a full course of treatment. This includes both curative treatment with artemisinin derivatives (following the withdrawal of chloroquine from the market) and eradicative treatment with primaquine, with the challenge of excluding G6PD deficiency. The aim of this paper is to describe the problems of malaria diagnosis and management in this unique territory, to highlight the adaptations made and to propose diagnostic, therapeutic and follow-up schemes adapted to the possibilities of access to the health system, with a view to homogenizing practices. This article also highlights the innovative strategies implemented in French Guiana to deal with this new epidemic: health mediation, mobile malaria team, rapid diagnostic tests and immediate out-of-hospital treatment Test and Treat, development of self-diagnosis and self-treatment. These proposals are part of a campaign to eliminate malaria in France in the short term.
La Guyane, dernier territoire endémique du paludisme en France, fait face à une recrudescence épidémique de paludisme depuis fin 2023. Cette épidémie, majoritairement causée par Plasmodium vivax, touche principalement des populations éloignées du système de soins. Elle a permis de mettre en lumière les difficultés de délivrance du traitement complet. Celui-ci comprend à la fois un traitement curatif de l'accès par dérivés de l'artémisinine (suite au retrait de la chloroquine du marché) et un traitement éradicateur par primaquine, avec les enjeux d’écarter un déficit en G6PD.
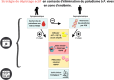
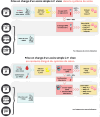
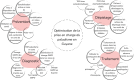
Ce travail a pour objectifs de décrire les problématiques de diagnostic et de prise en charge du paludisme sur ce territoire singulier, de mettre en avant les adaptations réalisées et de proposer des schémas diagnostiques, thérapeutiques et de suivi adaptés aux possibilités d'accès au système de soins dans un but d'homogénéisation des pratiques. Cet article a aussi pour dessein de souligner les stratégies innovantes mises en place en Guyane pour faire face à cette nouvelle épidémie : médiation en santé, équipe mobile « paludisme », tests diagnostiques rapides et traitement immédiat hors les murs Test and Treat, développement d'auto-diagnostic et d'auto-traitement. Ces propositions s'intègrent dans une volonté d’élimination du paludisme à court terme sur le territoire français.
Keywords: French Guiana; Malaria; Plasmodium vivax; Public health; Radical treatment; South America.
Copyright © 2025 SFMTSI.
Conflict of interest statement
Les auteurs déclarent ne pas avoir de liens d'intérêt.
Figures















References
-
- Alving AS, Arnold J, Hockwald RS, Clayman CB, Dern RJ, Beutler E, Flanagan CL. Potentiation of the curative action of primaquine in vivax malaria by quinine and chloroquine. J Lab Clin Med. 1955 Aug;46(2):301–6. PMID: 13242948. - PubMed
-
- Agence nationale de sécurité du médicament et des produits de santé (ANSM) Résumé des caractéristiques du produit (RCP) primaquine. 2021. 3 novembre,
-
- Agence nationale de sécurité du médicament et des produits de santé (ANSM) [cité 27 févr 2024]. ATU (Utilisation temporaire d'utilisation)/(Recommandation temporaire dutilisation)RTU - Primaquine.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
