Verruciform xanthoma: A case report and a review of recurrent cases
- PMID: 40248623
- PMCID: PMC12002571
- DOI: 10.4103/jomfp.jomfp_177_24
Verruciform xanthoma: A case report and a review of recurrent cases
Abstract
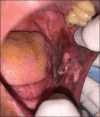
Oral verruciform xanthoma (VX) is an infrequently encountered benign lesion in the oral cavity. We report an unusual case of VX on the left buccal mucosa presented as a red and white exophytic mass with a greyish white diffuse patch associated with it. A differential diagnosis of papilloma, verrucous carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma associated with leukoplakia was listed. Histopathological findings were suggestive of VX due to the presence of characteristic foam cells in the connective tissue papillae. Immunohistochemical analysis with CD68 showed strong positive immunoreactivity revealing expression of foam cells. After the excisional biopsy, the patient was followed up for the next 6 months with no recurrence. Follow-up is very essential in such a case as the exophytic lesion was associated with a potentially malignant disorder. A short review of reported recurrent cases of verruciform xanthoma is also discussed.
Keywords: Foam cells; IHC; verruciform xanthoma; verrucous lesions.
Copyright: © 2025 Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Verruciform xanthoma associated with lichen planus.Autops Case Rep. 2022 Feb 21;12:e2021360. doi: 10.4322/acr.2021.360. eCollection 2022. Autops Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35252052 Free PMC article.
-
Verruciform xanthoma of the oral cavity - a case report.J Clin Diagn Res. 2013 Aug;7(8):1799-801. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2013/6559.3309. Epub 2013 Jul 19. J Clin Diagn Res. 2013. PMID: 24086918 Free PMC article.
-
Insight into verruciform xanthoma with oral submucous fibrosis: Case report and review of literature.J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2019 Feb;23(Suppl 1):43-48. doi: 10.4103/jomfp.JOMFP_210_18. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2019. PMID: 30967723 Free PMC article.
-
Oral verruciform xanthoma and erythroplakia associated with chronic graft-versus-host disease: a rare case report and review of the literature.BMC Res Notes. 2017 Nov 28;10(1):631. doi: 10.1186/s13104-017-2952-7. BMC Res Notes. 2017. PMID: 29183344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Verruciform Genital-Associated (Vegas) Xanthoma: report of a patient with verruciform xanthoma of the scrotum and literature review.Dermatol Online J. 2015 Aug 15;21(8):13030/qt7kb930rf. Dermatol Online J. 2015. PMID: 26437158 Review.
References
-
- Shafer WG. Verruciform xanthoma. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1971;31:784–9. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
