Complications and management of patients with liver hydatid cyst: A single center experience
- PMID: 40248675
- PMCID: PMC11999902
- DOI: 10.14744/hf.2024.2024.0052
Complications and management of patients with liver hydatid cyst: A single center experience
Abstract
Background and aim: Hydatid cysts are caused by Echinococcus larvae and are prevalent in endemic areas worldwide. We analyzed post-procedure complications and outcomes of patients with liver hydatid cysts.
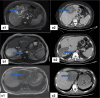
Materials and methods: We included patients who were managed either by surgery or percutaneous drainage (PAIR) for hydatid liver cysts at Harran University Faculty of Medicine Hospital between January 2017 and February 2021. We recorded age, sex, segmental location, size, number, Gharbi classification, treatment modality, length of hospital stays, and complications.
Results: We included a total of 209 patients who were managed by hydatid liver cysts. Among them, 74 post-procedural complications were developed in a total of 69 (33%) patients. Biliary fistula was the most prevalent complication (n=38,18.2%). Hospitalization duration was a median of 5 days (2-36) and was 5 days (2-36) in patients who underwent surgery and 3 days (range:2-7) in patients managed by PAIR. Patients with cyst diameter ≥9.5 cm were predicted to have an increased risk of complications with 70% sensitivity and 60% specificity. More patients experienced any difficulties in patients who were managed by PAIR than those who underwent surgery (65.4% vs 28.4%, p<0.001).
Conclusion: Our study showed that both surgery and PAIR are safe and effective management strategies for patients with liver cyst hydatid. PAIR was associated with more complications but a shorter duration of hospitalization.
Keywords: Liver hydatid cyst surgery; percutaneous hydatid cyst treatment; post-operative complications.
© Copyright 2025 by Hepatology Forum.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Current approaches in the surgical treatment of liver hydatid disease: single center experience.BMC Surg. 2019 Jul 17;19(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s12893-019-0553-1. BMC Surg. 2019. PMID: 31315619 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic hydatid: PAIR, drain or resect?J Gastrointest Surg. 2011 Oct;15(10):1829-36. doi: 10.1007/s11605-011-1649-9. Epub 2011 Aug 9. J Gastrointest Surg. 2011. PMID: 21826545
-
Biliary fistula after treatment for hydatid disease of the liver: when to intervene.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Jan 21;19(3):355-61. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i3.355. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23372357 Free PMC article.
-
Uniportal Video-assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (u-VATS) for Management of pulmonary hydatid cyst: A systematic review.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022 Mar 3;75:103474. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2022.103474. eCollection 2022 Mar. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022. PMID: 35386784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review of the treatment of liver hydatid cysts.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jan 7;21(1):124-31. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i1.124. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25574085 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Eckert J, Gemmell M, Meslin Fo-X, Pawlowski Z. 2001. WHO/OIE manual on echinococcosis in humans and animals: a public health problem of global concern World Organisation for Animal Health.
-
- Thompson RCA. Biology and Systematics of Echinococcus. In: Thompson RCA, lymbery AJ, editors. Echinococcus and hydatid disease. Guilford: Biddles Ltd; 1995. pp. 1–37.
-
- Yılmaz GR, Babur C. Diagnosis of echinococcosis. Turk Bullet Hygiene Exp Biol. 2007;64(3):35–44.
-
- Çaycı M, Tihan D. Karaciğer kist hidatik tedavisinde güncel yaklaşım. Uludağ Üniv Tıp Fak Derg. 2016;42(1):53–59.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
