The role of exosomal lncRNAs in cardiovascular disease: Emerging insights based on molecular mechanisms and therapeutic target level
- PMID: 40248838
- PMCID: PMC12004008
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2024.10.001
The role of exosomal lncRNAs in cardiovascular disease: Emerging insights based on molecular mechanisms and therapeutic target level
Abstract
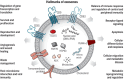
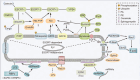
Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) are widely recognized as a leading cause of death worldwide; however, early diagnosis and disease progression monitoring play a crucial role in their clinical management. The common diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers have represented a revolutionary tool for studying CVD; however, their applications are limited to invasive irreversible heart diseases, such as drug-induced myocardial injury. In light of this information, a growing number of studies are currently investigating the diagnostic and prognostic potential of novel CVD biomarkers. Examples of this are long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) and other RNAs that are specifically expressed at the early stages of heart disease. These RNAs have been reported to be involved in the development of CVD via activating or inhibiting inflammatory mediators and angiogenesis-related factors, as well as endothelial cell proliferation, migration and phenotypic transformation. This review collectively summarizes the recent studies' results concerning exosomal lncRNA biogenesis, characterization, and function, as well as its role as a novel biomarker in a variety of CVD.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Cardiovascular diseases; Drugs; Exosomes; LncRNA.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Mengyun Gu, Lei Shi, Zixuan Yang, Minhui Zheng, Yan Wang and Naping Tang are currently employed by Shanghai Innostar Bio-Technology Co., Ltd. Liyuan Zhao, Zhimin Sun, Luyao Sun, Gang Liu, Feng Miao are currently employed by InnoStar Bio-tech Nantong Co., Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
New Developments in Exosomal lncRNAs in Cardiovascular Diseases.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Jul 8;8:709169. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.709169. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34307511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights on the Biomarker Potential of Exosomal Non-Coding RNAs in Colorectal Cancer: An In Silico Characterization of Related Exosomal lncRNA/circRNA-miRNA-Target Axis.Cells. 2023 Apr 4;12(7):1081. doi: 10.3390/cells12071081. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37048155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological Function of Long Non-coding RNA (LncRNA) Xist.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 10;9:645647. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.645647. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34178980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor-Derived Exosomal Non-Coding RNAs: The Emerging Mechanisms and Potential Clinical Applications in Breast Cancer.Front Oncol. 2021 Oct 11;11:738945. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.738945. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34707990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The functional roles of exosomal long non-coding RNAs in cancer.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 Jun;76(11):2059-2076. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03018-3. Epub 2019 Jan 25. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 30683984 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Qishuo T., Youyou Z., Jie Z., Yalei Y., Wei Z., Quan L., Liang L., Liang R. Role of the heat shock protein family in chlorpromazine-induced cardiotoxicity. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2023;43:1064–1072. - PubMed
-
- Abukhalil M.H., Hussein O.E., Aladaileh S.H., Althunibat O.Y., Al-Amarat W., Saghir S.A., Alfwuaires M.A., Algefare A.I., Alanazi K.M., Al-Swailmi F.K., et al. Visnagin prevents isoproterenol-induced myocardial injury by attenuating oxidative stress and inflammation and upregulating Nrf2 signaling in rats. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2021;35 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

