Nutrient starvation-induced Hda1C rewiring: coordinated regulation of transcription and translation
- PMID: 40248913
- PMCID: PMC12006795
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaf256
Nutrient starvation-induced Hda1C rewiring: coordinated regulation of transcription and translation
Abstract
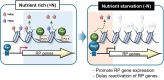
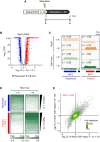
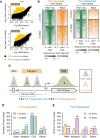
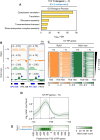
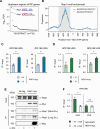
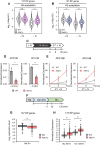
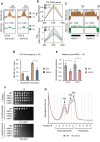
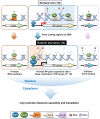
In yeast, Hda1 histone deacetylase complex (Hda1C) plays an important role in transcriptional regulation by modulating histone acetylation. We here explored the changes in Hda1C binding in nutrient-rich and -starved conditions. Chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing revealed that starvation alters RNA Pol II and Hda1C binding to coding genes in a highly correlated manner. Interestingly, we discovered RNA Pol II transcription-independent recruitment of Hda1C to intergenic regions, particularly the upstream regulatory sequences (URS) of ribosomal protein (RP) genes, which are enriched with Rap1 binding sites. Under nutrient starvation, Rap1 contributes to the recruitment of Hda1C to these URS regions, where Hda1C deacetylates histones, thereby fine-tuning basal gene expression and delaying RP gene reactivation. Furthermore, Hda1C is also required for RNA Pol I transcription of ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs) and RNA Pol III transcription of transfer RNA (tRNA) genes, especially in nutrient-limited conditions. Significantly, Hda1C mutants are sensitive to translation inhibitors and display altered ribosome profiles. Thus, Hda1C may coordinate transcriptional regulation within the nucleus with translation control in the cytoplasm and could be a key regulator of gene expression responses to nutrient stress.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transcription-dependent targeting of Hda1C to hyperactive genes mediates H4-specific deacetylation in yeast.Nat Commun. 2019 Sep 19;10(1):4270. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12077-w. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31537788 Free PMC article.
-
The Hda1 histone deacetylase limits divergent non-coding transcription and restricts transcription initiation frequency.EMBO J. 2021 Dec 1;40(23):e108903. doi: 10.15252/embj.2021108903. Epub 2021 Oct 18. EMBO J. 2021. PMID: 34661296 Free PMC article.
-
Opposing functions of the Hda1 complex and histone H2B mono-ubiquitylation in regulating cryptic transcription in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.G3 (Bethesda). 2021 Oct 19;11(11):jkab298. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkab298. G3 (Bethesda). 2021. PMID: 34499735 Free PMC article.
-
Histone H4-Specific Deacetylation at Active Coding Regions by Hda1C.Mol Cells. 2020 Oct 31;43(10):841-847. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2020.0141. Mol Cells. 2020. PMID: 32913143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The multifunctional transcription factor Rap1: a regulator of yeast physiology.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2016 Jun 1;21(5):918-30. doi: 10.2741/4429. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2016. PMID: 27100480 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

