Correlation of extracellular vesicle Alu RNA with brain aging and neuronal injury: a potential biomarker for brain aging
- PMID: 40248949
- PMCID: PMC12010651
- DOI: 10.1080/07853890.2025.2493767
Correlation of extracellular vesicle Alu RNA with brain aging and neuronal injury: a potential biomarker for brain aging
Abstract
Background: Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are promising biomarkers for neurodegeneration. Alu elements are retrotransposons increasingly expressed with age and may be involved in aging-related diseases.
Objective: To determine the potential of Alu RNA in plasma-derived EVs as a biomarker for brain aging and neuronal injury.
Methods: EVs were isolated from plasma samples across different age groups. EV Alu RNA levels were measured and their associations with biomarkers of brain aging, including plasma neurofilament light chain (NfL), plasma amyloid-beta (Aβ42 and Aβ40), and plasma phosphorylated tau (p-Tau181), were analyzed.
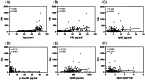
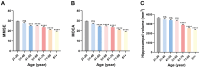
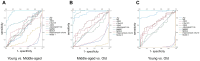
Results: EV Alu RNA levels were increased significantly with age and were strongly correlated with plasma NfL, suggesting a strong association between EV Alu RNA and neuronal injury. Significant correlations were also found between EV Alu RNA and plasma amyloid-beta levels, while no significant association was observed with tau pathology.
Conclusions: EV Alu RNA levels are elevated with age and associated with neuronal injury, highlighting their potential as a novel, non-invasive biomarker for brain aging and neurodegeneration.
Keywords: Extracellular vesicle; alu RNA; biomarker; brain aging; neurodegeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
