Do cell culturing influence the radiosensitizing effect of gold nanoparticles: a Monte Carlo study
- PMID: 40249448
- PMCID: PMC12008099
- DOI: 10.1186/s40658-025-00746-3
Do cell culturing influence the radiosensitizing effect of gold nanoparticles: a Monte Carlo study
Abstract
Background: Cell culture can be categorized into two major types: adherent and suspension. Both are used in a range of diverse research applications, exhibiting Pros and Cons, depending on what is being studied. In the field of Internal Emitters (IE), different morphological features such as nuclei size, cytoplasm ratio, and shape could influence its non-uniformity deposition and thus impact on the biological outcome. In this work we tested the hypothesis that cellular morphology differences, offered by adherent and suspension cultures, influence the radiosensitizing effect of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs).
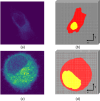
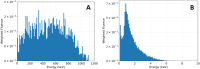
Methods: Using two PC3 cellular models, taken using confocal microscopy, we conducted Monte Carlo simulations to investigate the effects of different irradiation conditions on cellular Survival Fractions (SF). Our simulations focused on cells exposed to two distinct irradiation sources: 60Co and 14 MeV protons, along both the longer and shorter axes of the cells to assess directional influences on cell survival. Additionally, we compared the SF of cells adherent to the culture flask with those in suspension, reflecting different experimental and potentially clinical scenarios.
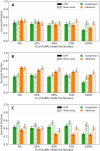
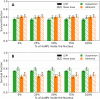
Results: In the absence of AuNPs, neither cell type nor irradiation direction significantly affected SF for the radiation types tested. However, with AuNPs present, SF demonstrated a strong dependence on irradiation direction and cell morphology.
Conclusions: Our results indicate that the direction of irradiation plays a crucial role in determining the effectiveness of AuNPs in reducing SF. Furthermore, the results suggest that using cells in suspension will reduce the dependence of cell survival on the beam direction during irradiation, regardless of the radiation quality used.
Keywords: Cell culturing; Cell survival fraction; Direction of irradiation; Gold nanoparticles; Monte Carlo simulation; Radiosensitizers; Realistic cell model.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Gallez B. Radiosensitization. Encyclopedia of Cancer [Internet]. Springer Berlin Heidelberg; 2011. pp. 3154–7. Available from: 10.1007/978-3-642-16483-5_4924
-
- Howard D, Sebastian S, Le QV-C, Thierry B, Kempson I. Chemical Mechanisms of Nanoparticle Radiosensitization and Radioprotection: A Review of Structure-Function Relationships Influencing Reactive Oxygen Species. Int J Mol Sci [Internet]. 2020;21:579. Available from: 10.3390/ijms21020579 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Moradi F, Rezaee Ebrahim Saraee K, Abdul Sani SF, Bradley DA. Metallic nanoparticle radiosensitization: The role of Monte Carlo simulations towards progress. Radiation Physics and Chemistry [Internet]. 2021;180:109294. Available from: 10.1016/J.RADPHYSCHEM.2020.109294
-
- Schuemann J, Bagley AF, Berbeco R, Bromma K, Butterworth KT, Byrne HL et al. Roadmap for metal nanoparticles in radiation therapy: current status, translational challenges, and future directions. Physics in Medicine & Biology [Internet]. 2020;65:21RM02. Available from: 10.1088/1361-6560/ab9159 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

