Fit accuracy assessment of removable partial denture frameworks produced by direct metal laser sintering - a clinical trial
- PMID: 40249516
- PMCID: PMC12008063
- DOI: 10.1007/s00784-025-06336-y
Fit accuracy assessment of removable partial denture frameworks produced by direct metal laser sintering - a clinical trial
Abstract
Objectives: The purpose of this cross-over clinical study was to compare the number of framework repetitions, percentage of framework components adjusted, clinical acceptability, and fit accuracy of removable partial denture frameworks produced by the direct metal laser sintering technique (DMLS) and conventional technique.
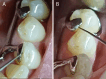
Materials and methods: For each dental arch (n = 26), two cobalt-chromium frameworks were produced through two protocols: direct metal laser sintering (experimental group) and conventional lost-wax casting technique (control group). The number of framework repetitions, the percentage of components that had to be adjusted, and the clinical acceptability were registered. The fit accuracy of functional components was assessed by a qualitative method using endodontic files to identify maladjustments and compared to a quantitative method based on silicone specimens digitized by micro-computed tomography. The normality was checked (Shapiro-Wilk test), and data were analyzed with McNemar, Wilcoxon and paired-t tests (α = 0.05).
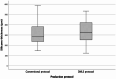
Results: No statistically significant differences were found between conventional and digital frameworks for most of the variables tested (p > 0.05) except the fewer laboratory repetitions (p = 0.046), higher percentage of components adjusted (p = 0.011), and better reciprocal arms fit (p = 0.044) in the frameworks produced by DMLS protocol. No statistically significant (p = 0.174) difference was found between the fit accuracy qualitative and quantitative assessment methods.
Conclusions: The DMLS and conventional protocols were similar. Despite the DMLS protocol exhibiting a higher percentage of components adjusted, it presented better reciprocal arms fit accuracy with no framework repetition.
Clinical relevance: Metal frameworks can be produced using DMLS eliminating casting problems.
Keywords: Accuracy; Computer-Aided design; Computer-Aided manufacturing; Direct metal laser sintering; Removable partial dentures.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Accuracy of Removable Partial Denture Frameworks Fabricated Using Conventional and Digital Technologies.Eur J Prosthodont Restor Dent. 2022 May 29;30(2):76-86. doi: 10.1922/EJPRD_2285Muehlemann11. Eur J Prosthodont Restor Dent. 2022. PMID: 34223713
-
Comparison of the overall fit of three-unit posterior fixed dental prostheses fabricated with laser sintering and conventional casting methods.Clin Oral Investig. 2025 Feb 24;29(3):153. doi: 10.1007/s00784-025-06221-8. Clin Oral Investig. 2025. PMID: 39988584 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptation of removable partial denture rest seats in prostheses made with selective laser sintering or casting techniques: A randomized clinical trial.J Prosthet Dent. 2024 Jul;132(1):108-114. doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2022.05.006. Epub 2022 Jun 30. J Prosthet Dent. 2024. PMID: 35786347 Clinical Trial.
-
Fit Accuracy of Removable Partial Denture Frameworks Fabricated with CAD/CAM, Rapid Prototyping, and Conventional Techniques: A Systematic Review.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Sep 6;2021:3194433. doi: 10.1155/2021/3194433. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34532499 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy of CAD-CAM systems for removable partial denture framework fabrication: A systematic review.J Prosthet Dent. 2021 Feb;125(2):241-248. doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2020.01.003. Epub 2020 Mar 5. J Prosthet Dent. 2021. PMID: 32147252
Cited by
-
Optimization of Bond Strength Between Heat-Polymerized PMMA and Contemporary CAD/CAM Framework Materials: A Comparative In Vitro Study.Polymers (Basel). 2025 May 27;17(11):1488. doi: 10.3390/polym17111488. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40508730 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Husain NAH, Ozcan M, Shimmel M, Abou-Ayash S (2020) A digital cast free clinical workflow for oral rehabilitation with removable partial dentures: a dental technique. J Prosthet Dent 123(5):680–685. 10.1016/j.prosdent.2019.05.008 - PubMed
-
- Ye H, Ning J, Li M, Niu L, Yang J, Sun Y et al (2017) Preliminary clinical application of removable partial denture frameworks fabricated using computeraided design and rapid prototyping techniques. Int J Prosthodont 30(4):348–353. 10.11607/ijp.5270 - PubMed
-
- Muehlemann E, Husain NAH, Ozcan M (2024) Patient satisfaction and accuracy of partial denture frameworks fabricated using conventional and digital techniques. Eur J Prosthodont Restor Dent 32(1):65–74. 10.1922/EJPRD_2554Muehlemann10 - PubMed
-
- Bajunaid SO, Altwaim B, Alhassan M, Alammari R (2019) The fit accuracy of removable partial denture metal frameworks using conventional and 3D printed techniques: an in vitro study. J Contemp Dent Pract 20(4):476–481. 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2542 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

