Efficacy and safety of RC48 in combination with PD-1 inhibitors for the treatment of locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma: a single-center, real-world study
- PMID: 40249537
- PMCID: PMC12008086
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-025-02362-0
Efficacy and safety of RC48 in combination with PD-1 inhibitors for the treatment of locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma: a single-center, real-world study
Abstract
Objective: This study aims to assess the efficacy and safety of RC48 in combination with PD-1 inhibitors for patients diagnosed with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma (mUC).
Methods: A retrospective analysis was performed on clinical data from 53 patients with locally advanced or metastatic bladder cancer, who were treated at the First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College between January 2023 and December 2023. The cohort was stratified into two groups: the RC48 combined immunotherapy group (RC48 + PD-1, n = 27) and the conventional chemotherapy group (gemcitabine and cisplatin regimen, GP, n = 26).
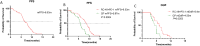
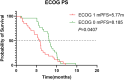
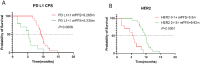
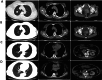
Results: The RC48 + PD-1 group demonstrated significantly higher objective response rates (ORR) and median progression-free survival (PFS) compared to the chemotherapy group (P < 0.05). Notably, the incidence of grade 3 or higher adverse events was elevated in the chemotherapy cohort, predominantly due to hematologic toxicities, with no treatment-related fatalities reported. In contrast, the RC48 combined PD-1 group primarily experienced immune-related adverse events, without any incidents of grade 3 or higher adverse effects or treatment-related deaths.
Conclusion: The combination of RC48 and PD-1 inhibitors exhibits promising antitumor activity and a manageable safety profile in patients with locally advanced or metastatic UC.
Keywords: Efficacy; Metastatic urothelial carcinoma; PD-1; RC48; Safety.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors indicate no financial or non-financial interests. Ethical approval: This study was conducted in accordance with the WMA Declaration of Helsinki and the CIOMS International Ethical Guidelines for Biomedical Research. The study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of The First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical University (Ethics Approval Number: Lunke Approval [2023] No. 331). Due to the retrospective nature of the study, Medical Ethics Committee of The First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical University waived the need of obtaining informed consent. Informed consent: The requirement for individual informed consent was waived by the committee due to the retrospective nature of the study.
Figures
References
-
- NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines). Bladder cancer, Version 2.2022. Fort Washington: National Comprehensive Cancer Network; 2022.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
