Association between prenatal environmental tobacco smoke exposure and preterm birth: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40249738
- PMCID: PMC12144600
- DOI: 10.1111/aogs.15126
Association between prenatal environmental tobacco smoke exposure and preterm birth: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: The purpose of this systematic review and meta-analysis is to evaluate the global risk of preterm birth associated with passive smoking. Specifically, the study aims to examine whether passive smoking continues to impact preterm birth rates, with particular attention to the potential effects following the implementation of stricter smoking bans in recent years.
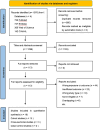
Material and methods: This systematic review and meta-analysis followed PRISMA guidelines and was preregistered in PROSPERO. A comprehensive literature search was conducted in PubMed, Embase, CINAHL, and Web of Science up to February 17, 2024, using keywords related to passive smoking and preterm birth. Eligible observational studies were selected, and data were independently extracted and assessed for quality by two authors. Statistical analysis used odds ratios (ORs) and the I2 statistic for heterogeneity. Subgroup analyses and publication bias assessments were conducted. Review Manager and Stata were used for the analysis, with significance set at p < 0.05.
Results: Meta-analysis showed a 21% increase in the odds of preterm birth in women exposed to environmental tobacco smoke (ETS) (OR, 1.21; 95% CI, 1.10-1.32) with significant heterogeneity (I2 = 76.2%). Stronger associations were found in cohort and cross-sectional studies, studies in Asia, larger sample sizes, and recent publications. Findings were robust across various analyses.
Conclusions: Prenatal environmental tobacco smoke exposure significantly increases preterm birth risk. Effective public health interventions, including stringent smoke-free policies, public education, and awareness campaigns, are needed to reduce environmental tobacco smoke exposure and improve maternal and infant health outcomes.
Keywords: anti‐smoking policy; meta‐analysis; prenatal environmental tobacco smoke exposure; preterm birth.
© 2025 The Author(s). Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Nordic Federation of Societies of Obstetrics and Gynecology (NFOG).
Conflict of interest statement
Ling Fan reports that financial support was provided by Liaoning Province Science and Technology Department. The rest of the authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (US); National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion (US); Office on Smoking and Health (US) . How Tobacco Smoke Causes Disease: the Biology and Behavioral Basis for Smoking‐Attributable Disease: A Report of the Surgeon General. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (US); 2010. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical