Impact of Simplera Sync™ sensors and Extended™ Wear Infusion Sets on glycaemia and system performance of the MiniMed™ 780G system in children and young adults with previously high HbA1c
- PMID: 40249764
- PMCID: PMC12151811
- DOI: 10.1111/dme.70048
Impact of Simplera Sync™ sensors and Extended™ Wear Infusion Sets on glycaemia and system performance of the MiniMed™ 780G system in children and young adults with previously high HbA1c
Abstract
Aims: The MiniMed™ 780G improves glycaemia and reduces burden in type 1 diabetes. We investigated how new all-in-one "Simplera Sync™" sensors and 7-day Extended™ Wear Infusion Sets (EIS) affect glycaemia and system performance in young people with previously elevated HbA1c levels (≥69 mmol/mol [≥8%]) after transitioning from 780G with Guardian 4™ sensors and 3-day infusion sets.
Methods: We conducted an extension phase analysis in 75 participants (aged 7-25 years) initially enrolled in the CO-PILOT randomised controlled trial. For this analysis, baseline was defined as the period following the use of 780G with Guardian 4™ sensors and 3-day infusion sets. Participants then transitioned to 780G with Simplera Sync™ and EIS. We compared glycaemic and system performance outcomes from baseline to those after the transition to 780G with Simplera Sync™ and EIS.
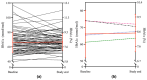
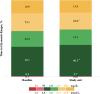
Results: Baseline HbA1c was 66.1 mmol/mol ± 14.2 mmol/mol and remained stable at 66.7 mmol/mol ± 11.2 mmol/mol after the transition (p = 0.38). Time in range (3.9-10.0 mmol/L [70-180 mg/dL]) at baseline was 58.5% ± 14.9% and 60.4% ± 15.7% after transition (p = 0.09). Time in tight range (3.9-7.8 mmol/L [70-140 mg/dL]) increased from 38.1% ± 13.1% at baseline to 40.5% ± 13.6% after the transition (p = 0.04). While using 780G with Simplera Sync™ and EIS, automation time increased from baseline 79.2% ± 25.9% to 85.8% ± 21.8% (p = 0.007), and sensor wear time from 80.7% ± 22.4% at baseline to 88.4% ± 17.2% (p < 0001).
Conclusions: Simplera Sync™ and EIS improved time in automation and sensor wear time when using 780G AHCL in this high-risk young population. This was associated with incremental improvement in time in tight range despite the challenges of this population.
Keywords: advanced hybrid closed loop; artificial pancreas; glycaemia; system performance; type 1 diabetes; youth.
© 2025 The Author(s). Diabetic Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Diabetes UK.
Conflict of interest statement
V.R.M. received research support from an Otago Medical School Endowment (University of Otago, New Zealand), the JDRF Australia Honours Scholarship (grant number 5‐SRA‐2021‐1088‐M‐X), and a Freemasons NZ Fellowship. B.J.W. and M.I.d.B. have in the past received honoraria, expenses, and research funding from Medtronic. C.J. and R.P. are the recipients of New Zealand Health Research Council (HRC) clinical practitioner research fellowships. No other potential conflicts of interest relevant to this study were reported.
Figures
References
-
- Michaels VR, Boucsein A, Watson AS, et al. Glucose and psychosocial outcomes 12‐months following transition from multiple daily injections to advanced hybrid closed loop in youth with type 1 diabetes and suboptimal glycemia. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2024;26(1):40‐48. doi: 10.1089/dia.2023.0334 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yuan CY, Kong YW, Amoore T, et al. Improved satisfaction while maintaining safety and high time in range (TIR) with a Medtronic investigational enhanced advanced hybrid closed‐loop (e‐AHCL) system. Diabetes Care. 2024;47(4):747‐755. - PubMed
-
- Boucsein A, Zhou Y, Haszard JJ, et al. Protocol for a prospective, multicenter, parallel‐group, open‐label randomized controlled trial comparing standard care with closed lOoP in chiLdren and yOuth with type 1 diabetes and high‐risk glycemic control: the CO‐PILOT trial. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2024;23:1397‐1407. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

