The pentameric chloride channel BEST1 is activated by extracellular GABA
- PMID: 40249777
- PMCID: PMC12037058
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2424474122
The pentameric chloride channel BEST1 is activated by extracellular GABA
Abstract
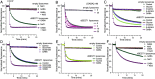
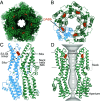
Bestrophin-1 (BEST1) is a chloride channel expressed in the eye and other tissues of the body. A link between BEST1 and the principal inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) has been proposed. The most appreciated receptors for extracellular GABA are the GABAB G-protein-coupled receptors and the pentameric GABAA chloride channels, both of which have fundamental roles in the central nervous system. Here, we demonstrate that BEST1 is directly activated by GABA. Through functional studies and atomic-resolution structures of human and chicken BEST1, we identify a GABA binding site on the channel's extracellular side and determine the mechanism by which GABA binding stabilizes opening of the channel's central gate. This same gate, "the neck," is activated by intracellular [Ca2+], indicating that BEST1 is controlled by ligands from both sides of the membrane. The studies demonstrate that BEST1, which shares no structural homology with GABAA receptors, is a GABA-activated chloride channel. The physiological implications of this finding remain to be studied.
Keywords: GABA; activation; bestrophin; chloride channel; receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures






Update of
-
The pentameric chloride channel BEST1 is activated by extracellular GABA.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 22:2024.11.22.624909. doi: 10.1101/2024.11.22.624909. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Apr 22;122(16):e2424474122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2424474122. PMID: 39605608 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Devi L. A., Fricker L. D., “Transmitters and peptides: Basic principles” in Neuroscience in the 21st Century: From Basic to Clinical, Pfaff D. W., Volkow N. D., Rubenstein J. L., Eds. (Springer International Publishing, Cham, 2022), pp. 2059–2075, 10.1007/978-3-030-88832-9_51. - DOI
-
- Simon J., Wakimoto H., Fujita N., Lalande M., Barnard E. A., Analysis of the set of GABA(A) receptor genes in the human genome. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 41422–41435 (2004). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R35 GM131921/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U24GM129539/HHS | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- SF349247/Simons Foundation (SF)
- R35GM131921/HHS | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- 5T32GM132081/HHS | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- T32 GM132081/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R24GM154192/HHS | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- U24 GM129539/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30CA008748/HHS | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- 25PRE1373036/American Heart Association (AHA)
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R24 GM154192/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

