The crosstalk of breast cancer and ischemic heart disease
- PMID: 40251177
- PMCID: PMC12008236
- DOI: 10.1038/s41420-025-02428-6
The crosstalk of breast cancer and ischemic heart disease
Abstract
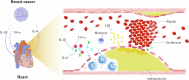
In recent years, the continuous optimization of anti-tumor therapy has greatly improved the cancer-specific survival rate for patients with breast cancer (BC). The prevention and treatment of breast cancer-related heart diseases have become a new breakthrough in improving the long-term survival for BC patient. The cardiac damages caused by BC treatment are increasingly prominent among BC patients, of which ischemic heart disease (IHD) is the most prominent. Besides, the systemic inflammatory response activated by tumor microenvironment c an induce and exacerbate IHD and increase the risk of myocardial infarction (MI). Conversely, IHD can also exert detrimental effects on tumors. MI not only increases the risk of BC, but also induces specialized immune cell to BC and accelerates the progression of BC. Meanwhile, the treatment of IHD can also promote BC metastasis and transition to more aggressive phenotypes. Although BC and IHD are diseases of two independent systems, their crosstalk increases the difficulty of anti-cancer treatment and IHD management, which reduces the survival for both diseases. Therefore, this review mainly explores the mutual influence and underlying mechanisms between BC and IHD, aiming to provide insights for improving the long-term survival for patients with BC or IHD.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Long-term risk of ischemic heart disease after adjuvant radiotherapy in breast cancer: results from a large population-based cohort.Breast Cancer Res. 2020 Jan 22;22(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s13058-020-1249-2. Breast Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 31969169 Free PMC article.
-
[Differences and similarities in ischemic heart disease in men and women].Folia Med Cracov. 1991;32(1-2):43-56. Folia Med Cracov. 1991. PMID: 1843699 Review. Polish.
-
E-Cigarettes Promote Macrophage-Tumor Cells Crosstalk: Focus on Breast Carcinoma Progression and Lung Metastasis.Explor Res Hypothesis Med. 2021 Jun;6(2):60-66. doi: 10.14218/erhm.2021.00002. Epub 2021 Feb 24. Explor Res Hypothesis Med. 2021. PMID: 35419501 Free PMC article.
-
Myocardial infarction and ischemic heart disease in overweight and obesity with and without metabolic syndrome.JAMA Intern Med. 2014 Jan;174(1):15-22. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.10522. JAMA Intern Med. 2014. PMID: 24217719
-
Breast cancer under age 40: a different approach.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2015 Apr;16(4):16. doi: 10.1007/s11864-015-0334-8. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25796377 Review.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49. - PubMed
-
- Magnoni F, Corso G. Progress in breast cancer surgical management. Eur J Cancer Prev. 2022;31:551–3. - PubMed
-
- Fisher B, Anderson S, Bryant J, Margolese RG, Deutsch M, Fisher ER, et al. Twenty-year follow-up of a randomized trial comparing total mastectomy, lumpectomy, and lumpectomy plus irradiation for the treatment of invasive breast cancer. N. Engl J Med. 2002;347:1233–41. - PubMed
-
- Valente SA, Shah C The Landmark Series: Adjuvant Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2020. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

