Mortality among individuals with chronic kidney disease based on the 2012 and 2021 KDIGO blood pressure targets
- PMID: 40251275
- PMCID: PMC12008221
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-91731-4
Mortality among individuals with chronic kidney disease based on the 2012 and 2021 KDIGO blood pressure targets
Abstract
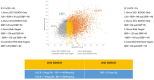
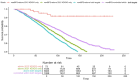
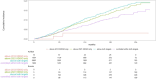
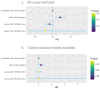
The 2021 Kidney Disease: Improving Global Prognosis (KDIGO) guidelines set a target systolic blood pressure (SBP) of 120 mmHg for chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients. This paper aims to compare mortality outcomes in CKD patients following the 2021 KDIGO guidelines versus the 2012 KDIGO guidelines. We used the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) database to categorize CKD patients into four groups: "above 2021 KDIGO only", "above 2012 KDIGO only", "above both targets" and "controlled with both targets". We compared differences in all-cause and cardiovascular deaths among these groups. In total, 10,612 CKD patients from the 2001-2018 NHANES database were identified. Subsequently, 2,226 patients lacking mortality information and 1,157 without crucial laboratory data were excluded. 7,229 CKD patients were enrolled, with 50.67% above both targets, 27.1% controlled within both targets, 1.01% above the 2012 KDIGO target, and 21.22% only above the 2021 KDIGO target. In multivariate analyses, the risk of all-cause mortality was not statistically significant (hazard ratio (HR): 0.91, 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.8-1.02, P = 0.11) for patients above the 2021 KDIGO target only compared to those controlled with both targets. Similar results were found for cardiovascular deaths. The 2021 KDIGO guidelines did not differentiate high-risk CKD populations in terms of all-cause death and cardiovascular death, compared with the 2012 KDIGO guidelines.
Keywords: Blood pressure; Chronic kidney disease; Guideline; Mortality; NHANES.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Institutional review board statement: NHANES protocol was approved by the Research Ethics Review Board of National Center for Health Statistics. All participants provided informed consent prior to participating in NHANES. The Ethical Approval Code/Number is available from the published NCHS Ethics Review Board (ERB) Approval online ( https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/irba98.htm#print ). Informed consent statement: Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in NHANES.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cardiovascular Implications of the 2021 KDIGO Blood Pressure Guideline for Adults With Chronic Kidney Disease.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022 May 3;79(17):1675-1686. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2022.02.040. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 35483755
-
Potential implications of the 2021 KDIGO blood pressure guideline for adults with chronic kidney disease in the United States.Kidney Int. 2021 Mar;99(3):686-695. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.12.019. Kidney Int. 2021. PMID: 33637204 Free PMC article.
-
Is the KDIGO Systolic Blood Pressure Target <120 mm Hg for Chronic Kidney Disease Appropriate in Routine Clinical Practice?Hypertension. 2022 Jan;79(1):4-11. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.121.18434. Epub 2021 Nov 17. Hypertension. 2022. PMID: 34784720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Suboptimal blood pressure control in chronic kidney disease stage 3: baseline data from a cohort study in primary care.BMC Fam Pract. 2013 Jun 24;14:88. doi: 10.1186/1471-2296-14-88. BMC Fam Pract. 2013. PMID: 23800117 Free PMC article.
-
KDOQI US commentary on the 2013 KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Lipid Management in CKD.Am J Kidney Dis. 2015 Mar;65(3):354-66. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2014.10.005. Epub 2014 Nov 18. Am J Kidney Dis. 2015. PMID: 25465166 Review.
References
-
- Whelton, P. K. et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: executive summary: a report of the American college of cardiology/american heart association task force on clinical practice guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol.71, 2199–2269 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Ku, E., Lee, B. J., Wei, J. & Weir, M. R. Hypertension in CKD: core curriculum 2019. Am. J. Kidney Dis.74, 120–131 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Keith, D. S., Nichols, G. A., Gullion, C. M., Brown, J. B. & Smith, D. H. Longitudinal follow-up and outcomes among a population with chronic kidney disease in a large managed care organization. Arch. Intern. Med.164, 659–663 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Stevens, P. E. & Levin, A. Evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease: synopsis of the kidney disease: improving global outcomes 2012 clinical practice guideline. Ann. Intern. Med.158, 825–830 (2013). - PubMed
-
- KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Blood Pressure in Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 99, S1–S87 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

