Genome wide identification of LcC2DPs gene family in Lotus corniculatus provides insights into regulatory network in response to abiotic stresses
- PMID: 40251318
- PMCID: PMC12008259
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-97896-2
Genome wide identification of LcC2DPs gene family in Lotus corniculatus provides insights into regulatory network in response to abiotic stresses
Abstract
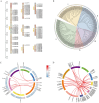
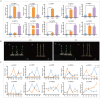
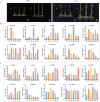
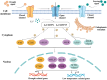
Low temperatures and drought reduce forage yield and quality, with protein kinases crucial for plant stress response. This study examines the LcC2DPs protein kinase family in Lotus corniculatus, identifying 90 members, with some tandemly distributed on chromosomes 2-6, and grouped into 5 subfamilies (I-V). 34 homologous gene pairs were found in Arabidopsis thaliana. LcC2DP genes promoters contain hormone and stress response elements. GO analysis highlights enrichment in hormone response and kinase activity. Transcriptomic analysis links 78 genes to environmental response and stress growth, with 10 validated by qRT-PCR after treatment with 100 μM ABA and IAA, 20% PEG6000, and 4 °C. Protein interaction analysis identifies 5 core proteins (LcC2DP5, 11, 15, 38, and 58) activated by drought and cold stress. Gene analysis revealed that only LcC2DP5 and LcC2DP15 share co-expression transcription factors, with bZIP, bHLH, WRKY, NAC, MYB-related, MYB, C3H, and C2H2 being prominent. These proteins are expressed under drought and cold conditions, highlighting LcC2DP5 and LcC2DP15 activity. NAC and C2H2 are vital for drought response, while bZIP and MYB-related are important for cold response. This suggests that various LcC2DPs in Lotus corniculatus respond to hormones and stress via a TF regulatory network.
Keywords: Lotus corniculatus; C2 domain; Calcium-dependent protein kinase; Cold stress; Drought response; Signal transduction.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Genome-wide identification of the Q-type C2H2 zinc finger protein gene family and expression analysis under abiotic stress in lotus (Nelumbo nucifera G.).BMC Genomics. 2024 Jun 28;25(1):648. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10546-1. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38943098 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of MYB Transcription Factor Family in Response to Various Abiotic Stresses in Coconut (Cocos nucifera L.).Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 18;25(18):10048. doi: 10.3390/ijms251810048. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337532 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and analysis of the WRKY gene family in Sainfoin (Onobrychis viciifolia) and their response to drought, salt, and alkali stress.BMC Genomics. 2025 May 2;26(1):437. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11646-2. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40316926 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification of the DOF Gene Family in Kiwifruit (Actinidia chinensis) and Functional Validation of AcDOF22 in Response to Drought Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 22;25(16):9103. doi: 10.3390/ijms25169103. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201789 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription Factors Interact with ABA through Gene Expression and Signaling Pathways to Mitigate Drought and Salinity Stress.Biomolecules. 2021 Aug 5;11(8):1159. doi: 10.3390/biom11081159. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34439825 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Staniak, M. The impact of drought stress on the yields and food value of selected forage grasses. Acta Agrobot.69, 1663. 10.5586/aa.1663 (2016).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- No. 2020-54/Cultivation Project of Guizhou University
- 32260338/Innovative Research Group Project of the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 31660685/Innovative Research Group Project of the National Natural Science Foundation of China,China
- 2023ZK119/the Guizhou Province Science and Technology Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

