Genome-wide identification and expression profiling of MYB transcription factors in Artemisia argyi
- PMID: 40251470
- PMCID: PMC12007207
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-025-11441-z
Genome-wide identification and expression profiling of MYB transcription factors in Artemisia argyi
Abstract
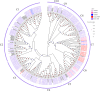
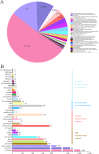
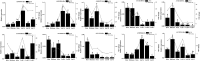
Artemisia argyi, a significant medicinal plant in China, is known for its high content of essential oils, flavonoids, and other bioactive compounds. MYB transcription factors are the largest gene family in plants and are widely reported to play important roles in plant development, metabolism, defense, and stress resistance. However, the MYB family of A. argyi has not been systematically studied. The aim of this study was to comprehensively analyze the MYB gene family of A. argyi and explore its potential role in flavonoid biosynthesis. Here, the phylogeny, chromosome location, gene structure, cis-acting elements, expression patterns and Gene ontology (GO) annotation of MYB gene family members were investigated using bioinformatics methods based on the whole-genome and transcriptome data of A. argyi. In total, 227 AYMYB transcription factors were identified from A. argyi genome, including 22 1R-MYB, 165 R2R3-MYB, 16 3R-MYB, 5 4R-MYB and 19 atypical MYB members. These AYMYBs were unevenly distributed across the A. argyi genome. Subcellular localization prediction revealed that all the AYMYBs were localized in the nucleus. The protein motifs, conserved domains, and gene structures of AYMYBs were identified, and the results showed that AYMYBs from the same subfamily exhibited similar motifs and gene structures. Cis-acting elements and GO analysis suggested that AYMYBs may be involved in many biological processes related to plant development, metabolism, defense, and stress resistance. Moreover, quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis showed that approximately 50 genes showed high expression levels in the leaves of A. argyi and AYMYBs showed specific expression patterns under MeJA treatment. Together, our research will offer useful information for future investigations into the functions of MYB genes in A. argyi, especially in regulating the process of flavonoid biosynthesis in leaves and in response to MeJA treatment.
Keywords: AYMYB; Artemisia argyi; Bioinformatics tools; Expression pattern; MeJA.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The cultivated A. argyi ‘Xiang Ai’ has been identified and preserved by the team of the corresponding author, Professor Dahui Liu. Therefore, we ensure that we have obtained permission from Professor Liu to collect and use A. argyi in this experiment. The collection of plant material complies with relevant institutional, national, and international guidelines and legislation. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
[Identification and expression analysis of members of R2R3-MYB transcription factors family in Artemisia argyi].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024 Aug;49(16):4407-4419. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20240415.103. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39307777 Chinese.
-
Genome-wide identification, characterization and expression pattern analysis of TIFY family members in Artemisia argyi.BMC Genomics. 2024 Oct 3;25(1):925. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10856-4. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39363209 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and expression profiling of MYB transcription factors against stresses and during male organ development in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis).Plant Physiol Biochem. 2016 Jul;104:200-15. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.03.021. Epub 2016 Mar 18. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27038155
-
[Genome-wide identification of bZIP family genes and screening of candidate AarbZIPs involved in terpenoid biosynthesis in Artemisia argyi].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023 Oct;48(19):5181-5194. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20230613.101. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 38114108 Chinese.
-
MYB Transcription Factors as Regulators of Phenylpropanoid Metabolism in Plants.Mol Plant. 2015 May;8(5):689-708. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2015.03.012. Epub 2015 Apr 1. Mol Plant. 2015. PMID: 25840349 Review.
References
-
- Dubos C, Stracke R, Grotewold E, et al. MYB transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci. 2010;15:573–81. - PubMed
-
- Du H, Zhang L, Liu L, et al. Biochemical and molecular characterization of plant MYB transcription factor family. Biochem (Mosc). 2009;74:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Simon M, Lee MM, Lin Y, et al. Distinct and overlapping roles of single-repeat MYB genes in root epidermal patterning. Dev Biol. 2007;311:566–78. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2023AFA032/HuBei Provincial Natural Science Foundation Innovative Group Project
- 82304660/National Natural Science Foundation of China Youth Program
- 2024M753648/China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
- 2024AFD228/Hubei Provincial Natural Science Foundation and Traditional Chinese Medicine Innovation and Development Joint Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

