Adjunctive therapies in orthodontics: a scoping systematic review
- PMID: 40251484
- PMCID: PMC12008976
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-025-05874-x
Adjunctive therapies in orthodontics: a scoping systematic review
Abstract
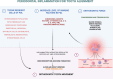
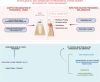
Background: Orthodontic tooth movement (OTM) induces physiological and sometimes pathological inflammation in periodontal tissues. This review evaluates the effectiveness of low-level laser therapy (LLLT), vibrational therapy, and probiotics as adjunctive treatments for managing inflammation, pain, and the duration of OTM.
Methods: Medline via OVID, Cochrane, EMBASE, and Web of Science databases were utilized to identify randomized controlled trials (RCTs) published between January 1990 and November 2023. Studies were selected based on their evaluation of LLLT, vibrational therapy, and probiotics as adjuncts in fixed orthodontic treatment.
Results: LLLT shows promise in enhancing orthodontic tooth movement by accelerating tooth movement and potentially reducing pain. However, disparate study outcomes indicate a need for standardized application protocols. The efficacy of vibrational therapy as an adjunct in OTM remains inconclusive. Some studies in this regard indicate a significant acceleration in OTM but most did not. Probiotic therapy shows potential to improve oral microbiota balance and inflammation but requires more rigorous studies to determine its efficacy and optimal administration methods.
Conclusion: Future research should focus on establishing standardized guidelines and protocols to achieve consistent and reliable outcomes across these adjunctive therapies.
Keywords: Fixed orthodontic treatment; Low level laser therapy; Orthodontic tooth movement; Probiotics; Vibrational therapy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical