Optimizing prediction of metastasis among colorectal cancer patients using machine learning technology
- PMID: 40251500
- PMCID: PMC12007332
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-025-03841-y
Optimizing prediction of metastasis among colorectal cancer patients using machine learning technology
Abstract
Background and aim: Colorectal cancer is among the most prevalent and deadliest cancers. Early prediction of metastasis in patients with colorectal cancer is crucial in preventing it from the advanced stages and enhancing the prognosis among these patients. So far, previous studies have been conducted to predict metastasis in colorectal cancer patients using clinical data. The current research attempts to leverage a combination of demographic, lifestyle, nutritional, and clinical factors, such as diagnostic and therapeutical factors, to construct an ML model with more predictive insights and generalizability than previous ones.
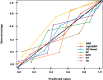
Materials and methods: In this retrospective study, we used 1156 CRC patients referred to the Masoud internal clinic in Tehran City from January 2017 to December 2023. The chosen machine learning algorithms, including LightGBM, XG-Boost, random forest, artificial neural network, support vector machine, decision tree, K-Nearest Neighbor and logistic regression, were utilized to establish prediction models for predicting metastasis among colorectal cancer patients. We also assessed features based on the best-performing model to improve clinical usability. To show the generalizability of the established prediction model for predicting CRC metastasis, we leveraged the data of 115 CRC patients from Imam Khomeini Hospital in Sari City. We assessed the predictive ability of LightGBM as the best-performing model based on external data.
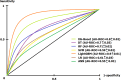
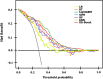
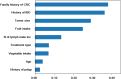
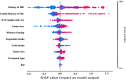
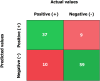
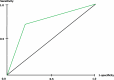
Results: The LightGBM model with a PPV of 97.32%, NPV of 84.67%, sensitivity of 83.14%, specificity of 93.14%, accuracy of 88.14%, F1-score of 87.51%, and an AU-ROC of 0.9 [Formula: see text]0.01 obtained satisfactory performance for prediction purposes on this topic. Factors including the history of IBD, family history of CRC, number of lymph nodes involved, fruit intake, and tumor size were considered as more strengthful predictors for metastasis in colorectal cancer and clinical usability. The external validation cohort showed a PPV of 0.8, NPV of 0.85, sensitivity of 0.78, specificity of 0.86, accuracy of 0.834, F1-score of 0.795, and AU-ROC of 0.77[Formula: see text]0.03, demonstrating satisfactory generalizability when leveraging external data from other clinical settings.
Conclusion: The current empirical results indicated that LighGBM has predictive competency that can be leveraged by physicians in clinical environments for early prediction of metastasis and enhanced prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer.
Clinical trial number: Not applicable.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; Lifestyle factor; Machine learning; Metastasis; Prediction model; Prognosis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the ethics committee of Tehran University of Medical Sciences (Reg No: 1398-F-280-3/98-10-03). All methods were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations. Informed consent was obtained from all subjects and/or their legal guardian(s). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prediction of one-year recurrence among breast cancer patients undergone surgery using artificial intelligence-based algorithms: a retrospective study on prognostic factors.BMC Cancer. 2025 May 26;25(1):940. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14369-5. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40419997 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Prediction Model for 5-year Survival of Colorectal Cancer.Cancer Inform. 2024 Sep 4;23:11769351241275889. doi: 10.1177/11769351241275889. eCollection 2024. Cancer Inform. 2024. PMID: 39238654 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative prediction of regional lymph node metastasis of colorectal cancer based on 18F-FDG PET/CT and machine learning.Ann Nucl Med. 2021 May;35(5):617-627. doi: 10.1007/s12149-021-01605-8. Epub 2021 Mar 18. Ann Nucl Med. 2021. PMID: 33738763
-
Application of machine learning for predicting lymph node metastasis in T1 colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2024 Sep 23;409(1):287. doi: 10.1007/s00423-024-03476-9. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2024. PMID: 39311932
-
Risk factors and risk prediction models for colorectal cancer metastasis and recurrence: an umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses of observational studies.BMC Med. 2020 Jun 26;18(1):172. doi: 10.1186/s12916-020-01618-6. BMC Med. 2020. PMID: 32586325 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

