The G-quadruplex ligand CX-5461: an innovative candidate for disease treatment
- PMID: 40251554
- PMCID: PMC12007140
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-025-06473-8
The G-quadruplex ligand CX-5461: an innovative candidate for disease treatment
Abstract
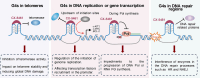
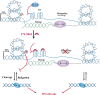
The ribosomal DNA (rDNA) plays a vital role in regulating protein synthesis by ribosome biogenesis, essential for maintaining cellular growth, metabolism, and more. Cancer cells show a high dependence on ribosome biogenesis and exhibit elevated rDNA transcriptional activity. CX-5461, also known as Pidnarulex, is a First-in-Class anticancer drug that has received 'Fast Track Designation' approval from the FDA. Initially reported to inhibit Pol I-driven rDNA transcription, CX-5461 was recently identified as a G-quadruplex structure (G4) stabilizer and is currently completed or undergoing multiple Phase I clinical trials in patients with breast and ovarian cancers harboring BRCA1/2, PALB2, or other DNA repair deficiencies. Additionally, preclinical studies have confirmed that CX-5461 demonstrates promising therapeutic effects against multifarious non-cancer diseases, including viral infections, and autoimmune diseases. This review summarizes the mechanisms of CX-5461, including its transcriptional inhibition of rDNA, binding to G4, and toxicity towards topoisomerase, along with its research status and therapeutic effects across various diseases. Lastly, this review highlights the targeted therapy strategy of CX-5461 based on nanomedicine delivery, particularly the drug delivery utilizing the nucleic acid aptamer AS1411, which contains a G4 motif to specifically target the highly expressed nucleolin on the surface of tumor cell membranes; It also anticipates the strategy of coupling CX-5461 with peptide nucleic acids and locked nucleic acids to achieve dual targeting, thereby realizing individualized G4-targeting by CX-5461. This review aims to provide a general overview of the progress of CX-5461 in recent years and suggest potential strategies for disease treatment involving ribosomal RNA synthesis, G4, and topoisomerase.
Keywords: CX-5461; Cancer; G-quadruplex; Ribosomal RNA; Ribosome biogenesis; Targeted therapy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: All the authors have provided their consent for publication of the manuscript. Competing interests: The authors declare they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Xu H, Hurley LH. A first-in-class clinical G-quadruplex-targeting drug. The bench-to-bedside translation of the fluoroquinolone QQ58 to CX-5461 (Pidnarulex). Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2022;77:129016. - PubMed
-
- Drygin D, Lin A, Bliesath J, Ho CB, O’Brien SE, Proffitt C, Omori M, Haddach M, Schwaebe MK, Siddiqui-Jain A, et al. Targeting RNA polymerase I with an oral small molecule CX-5461 inhibits ribosomal rna synthesis and solid tumor growth. Can Res. 2011;71:1418–30. - PubMed
-
- Scala F, Brighenti E, Govoni M, Imbrogno E, Fornari F, Treré D, Montanaro L, Derenzini M. Direct relationship between the level of p53 stabilization induced by rRNA synthesis-inhibiting drugs and the cell ribosome biogenesis rate. Oncogene. 2016;35:977–89. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

