Artificial intelligence (AI) in restorative dentistry: current trends and future prospects
- PMID: 40251567
- PMCID: PMC12008862
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-025-05989-1
Artificial intelligence (AI) in restorative dentistry: current trends and future prospects
Abstract
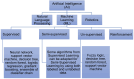
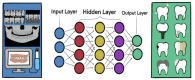
Background: Artificial intelligence (AI) holds immense potential in revolutionizing restorative dentistry, offering transformative solutions for diagnostic, prognostic, and treatment planning tasks. Traditional restorative dentistry faces challenges such as clinical variability, resource limitations, and the need for data-driven diagnostic accuracy. AI's ability to address these issues by providing consistent, precise, and data-driven solutions is gaining significant attention. This comprehensive literature review explores AI applications in caries detection, endodontics, dental restorations, tooth surface loss, tooth shade determination, and regenerative dentistry. While this review focuses on restorative dentistry, AI's transformative impact extends to orthodontics, prosthodontics, implantology, and dental biomaterials, showcasing its versatility across various dental specialties. Emerging trends such as AI-powered robotic systems, virtual assistants, and multi-modal data integration are paving the way for groundbreaking innovations in restorative dentistry.
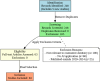
Methods: Methodologically, a systematic approach was employed, focusing on English-language studies published between 2020-2025(January), resulting in 63 peer-reviewed publications for analysis. Studies in caries detection, pedodontics, dental restorations, endodontics, tooth surface loss, and tooth shade determination highlighted AI trends and advancements. Inclusion criteria focused on AI applications in restorative dentistry, and publication timeframe. PRISMA guidelines were followed to ensure transparency in study selection, emphasizing on accuracy metrics and clinical relevance. The study selection process was carefully documented, and a flowchart of the stages, including identification, screening, eligibility, and inclusion, is shown in Fig. 1 to provide further clarity and reproducibility in the selection process.
Results: The review identified significant advancements in AI-driven solutions across multiple domains of restorative dentistry. Notable studies demonstrated AI's ability to achieve high diagnostic accuracy, such as up to 95% accuracy in caries detection, and its capacity to improve treatment planning efficiency, thus reducing patient chair time. Predictive analytics for personalized treatments was another area where AI has shown substantial promise.
Conclusion: The review discussed trends, challenges, and future research directions in AI-driven dentistry, highlighting the transformative potential of AI in optimizing dental care. Key challenges include data privacy concerns, algorithmic bias, interpretability of AI decision-making processes, and the need for standardized AI training programs in dental education. Further research should focus on integrating AI with emerging technologies like 3D printing for personalized restorations, and developing AI training programs for dental professionals.
Clinical significance: The integration of AI into restorative dentistry offers precision-driven solutions for improved patient outcomes. By enabling faster diagnostics, personalized treatment approaches, and preventive care strategies, AI can significantly enhance patient-centered care and clinical efficiency. This review contributes to advancing the understanding and implementation of AI in dental practice by synthesizing key findings, identifying trends, and addressing challenges.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Artificial neural networks; Caries detection; Deep learning; Machine learning; Restorative dentistry.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Artificial Intelligence in Aesthetic Medicine: Applications, Challenges, and Future Directions.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025 Jun;24(6):e70241. doi: 10.1111/jocd.70241. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 40501296 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Transformative Role of Artificial Intelligence in Dentistry: A Comprehensive Overview. Part 1: Fundamentals of AI, and its Contemporary Applications in Dentistry.Int Dent J. 2025 Apr;75(2):383-396. doi: 10.1016/j.identj.2025.02.005. Epub 2025 Mar 11. Int Dent J. 2025. PMID: 40074616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Smart Smile: Revolutionizing Dentistry With Artificial Intelligence.Cureus. 2023 Jun 30;15(6):e41227. doi: 10.7759/cureus.41227. eCollection 2023 Jun. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37529520 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Applications, functions, and accuracy of artificial intelligence in restorative dentistry: A literature review.J Esthet Restor Dent. 2023 Sep;35(6):842-859. doi: 10.1111/jerd.13079. Epub 2023 Jul 31. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2023. PMID: 37522291 Review.
-
Artificial Intelligence, the Digital Surgeon: Unravelling Its Emerging Footprint in Healthcare - The Narrative Review.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2024 Aug 15;17:4011-4022. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S482757. eCollection 2024. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2024. PMID: 39165254 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploration of AI-Powered Tools for Risk Assessment in General Dentistry.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2025 Jun;17(Suppl 2):S1270-S1272. doi: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_83_25. Epub 2025 Jun 18. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2025. PMID: 40655801 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Binhuraib H, Aloqayli S, Alkhalifah S, Aljohani A, Alotaibi R, Almalki R, et al. Digital shade matching techniques in fixed prosthodontics. J Healthc Sci. 2024;04(01):34–40.
-
- Babu A, Andrew Onesimu J, Martin Sagayam K. Artificial Intelligence in dentistry: Concepts, Applications and Research Challenges. Krit S, editor. E3S Web Conf. 2021;297:01074.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources