The effects of different exercise training protocols on mitochondrial dynamics in skeletal and cardiac muscles of Wistar rats
- PMID: 40251584
- PMCID: PMC12008994
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-025-05809-w
The effects of different exercise training protocols on mitochondrial dynamics in skeletal and cardiac muscles of Wistar rats
Abstract
Background: Mitochondrial fission and fusion both contribute to maintaining mitochondrial function and optimizing bioenergetic capacity.
Objective: The aim of this study was to compare the effect of aerobic and resistance training on mitochondrial fission and fusion markers in skeletal and cardiac muscles of Wistar rats.
Method: 24 male Wistar rats were randomly divided into four groups of moderate-intensity interval training (MIIT), high-intensity interval training (HIIT), resistance training (RT) and control (CON). The MIIT and HIIT groups performed treadmill exercises with an intensity of 60-65% and 80-85% of the maximum speed, respectively, while the RT group performed resistance training with an intensity of 30-60% of the rat's body weight for 8 weeks. The soleus (SOL), extensor digitorum longus (EDL) and left ventricular tissues were used to evaluate markers of mitochondrial fission and fusion PGC-1α (fusion/fission), Opa-1 (fusion), Fis-1 (fission), Drp-1 (fission), Mfn-1 and Mfn-2 (fusion) genes expression.
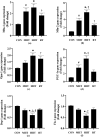
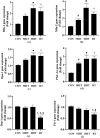
Results: In all three tissues, a significant increase in some mitochondrial fusion markers was observed after 8 weeks of training (p = < 0.0001-0.0452). Furthermore, a significant decrease in cardiac mitochondrial fission markers was observed in all three groups (p = < 0.0001-0.0156). This reduction in some markers was evident in the SOL tissue of the HIIT group (p < 0.0001 for Drp-1 and p = 0.0007 for Fis-1) and in the EDL tissue of the RT group (p = 0.0005 for Fis-1 and p = 0.0012 for Drp-1). The mitochondrial fission/fusion markers in the heart (p = 0.0007-0.0449) and SOL (p = 0.0050-0.0258) tissues of the HIIT group had more changes than the RT group, while the mitochondrial fission markers in the EDL tissue of the RT group had a lower level than the HIIT (p = 0.0087 for Drp-1) and MIIT (p = 0.0130 for Fis-1 and p = 0.0010 for Drp-1) groups.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrated that HIIT, through better regulation of mitochondrial fusion and fission than RT, improves mitochondrial dynamics in cardiac and SOL tissues.
Keywords: Exercise; Mitochondrial dynamics; Muscles; Myocardium; Rats.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval: The animal study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Hakim Sabzevari University (protocol code IR.HSU.AEC.1401.017 on January 21th, 2023). Consent for publication: Not applicable in this section. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

