Meta-analysis of arterial spin labeling MRI to identify residual cerebral arteriovenous malformations after treatment
- PMID: 40251605
- PMCID: PMC12007328
- DOI: 10.1186/s12880-025-01668-3
Meta-analysis of arterial spin labeling MRI to identify residual cerebral arteriovenous malformations after treatment
Abstract
Background: To use of statistical methods to assess the diagnostic value of arterial spin labeling (ASL) imaging for follow-up of treated arteriovenous malformations.
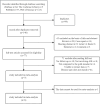
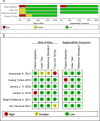
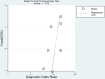
Methods: We screened references from four databases, namely, the Cochrane Library, PubMed, Web of Science and Embase, that met the requirements. The methodology quality of the included studies was evaluated using the QUADAS-2 (Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies-2) tool. Data pertaining to diagnostic performance were extracted, and the pooled sensitivity and specificity were calculated using a bivariate mixed-effects model.
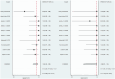
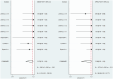
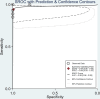
Results: We included six studies with a total of 132 patients with arteriovenous malformation (AVM). The merged sensitivity and specificity of ASL for the diagnosis of brain AVMs with incomplete occlusion after treatment were 0.94[0.86-0.98] and 0.99 [0.59-1.00], respectively. According to the SROC curve summary, the AUC was found to be 0.98 [0.96-0.99]. No significant publication bias was observed.
Conclusion: While ASL does not currently match the diagnostic precision of DSA, it is instrumental in post-treatment surveillance of AVM patients. With the development of ASL technology in the future, this technique holds promise as a minimally invasive diagnostic strategy for AVMs with fewer side effects.
Registration number of prospero: CRD42023422087.
Clinical trial number: Not applicable.
Keywords: Arterial spin labeling; Brain arteriovenous malformations; Meta-analysis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Human ethics and consent to participant: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Arterial-spin labeling MRI identifies residual cerebral arteriovenous malformation following stereotactic radiosurgery treatment.J Neuroradiol. 2020 Feb;47(1):13-19. doi: 10.1016/j.neurad.2018.12.004. Epub 2019 Jan 15. J Neuroradiol. 2020. PMID: 30658138
-
Diagnostic accuracy of arterial spin labeling MR imaging in detecting cerebral arteriovenous malformations: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Neurosurg Rev. 2024 Aug 27;47(1):492. doi: 10.1007/s10143-024-02659-8. Neurosurg Rev. 2024. PMID: 39190141
-
Evaluating post-treatment residual intracranial arteriovenous shunting: a comparison of arterial spin labeling MRI and digital subtraction angiography.Neuroradiology. 2025 May;67(5):1233-1250. doi: 10.1007/s00234-025-03548-7. Epub 2025 Feb 6. Neuroradiology. 2025. PMID: 39912896 Free PMC article.
-
Arterial spin labeling magnetic resonance imaging: toward noninvasive diagnosis and follow-up of pediatric brain arteriovenous malformations.J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2015 Apr;15(4):451-8. doi: 10.3171/2014.9.PEDS14194. Epub 2015 Jan 30. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2015. PMID: 25634818
-
Diagnostic value of arterial spin labeling for Alzheimer's disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2024 Nov 21;19(11):e0311016. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0311016. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39570963 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen CJ, Ding DL, Derdeyn CP, Lanzino G, Friedlander RM, Southerland AM, et al. Brain arteriovenous malformations A review of natural history, pathobiology, and interventions. Neurology. 2020;95:917–27. - PubMed
-
- Hofmeister C, Stapf C, Hartmann A, Sciacca RR, Mansmann U, terBrugge K, et al. Demographic, morphological, and clinical characteristics of 1289 patients with brain arteriovenous malformation. Stroke. 2000;31:1307–10. - PubMed
-
- Rosenkranz M, Regelsberger J, Zeumer H, Grzyska U. Management of cerebral arteriovenous malformations associated with symptomatic congestive intracranial hypertension. Eur Neurol. 2008;59:62–6. - PubMed
-
- Achrol AS, Guzman R, Varga M, Adler JR, Steinberg GK, Chang SD. Pathogenesis and radiobiology of brain arteriovenous malformations: implications for risk stratification in natural history and posttreatment course. NeuroSurg Focus. 2009;26:E9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- No.61601056/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- No.2019-JBY-TD-003/The Special Funds for Basic Research Funds for Central Universities Special Project
- DZMKJCX-2020-002/Beijing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine Dongzhimen Hospital Science and Technology Innovation Project Funding Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

