Decoding tumor angiogenesis: pathways, mechanisms, and future directions in anti-cancer strategies
- PMID: 40251641
- PMCID: PMC12007322
- DOI: 10.1186/s40364-025-00779-x
Decoding tumor angiogenesis: pathways, mechanisms, and future directions in anti-cancer strategies
Abstract
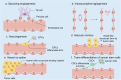
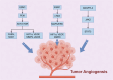
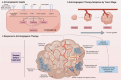
Angiogenesis, a crucial process in tumor growth and metastasis, necessitates targeted therapeutic intervention. This review reviews the latest knowledge of anti-angiogenesis targets in tumors, with emphasis on the molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways that regulate this process. We emphasize the tumor microenvironment's role in angiogenesis, examine endothelial cell metabolic changes, and evaluated potential therapeutic strategies targeting the tumor vascular system. At the same time, we analyzed the signaling pathway and molecular mechanism of tumor angiogenesis in detail. In addition, this paper also looks at the development trend of tumor anti-angiogenesis drugs, including their future development direction and challenges, aiming to provide prospective insight into the development of this field. Despite their potential, anti-angiogenic therapies encounter challenges like drug resistance and side effects, necessitating ongoing research to enhance cancer treatment strategies and the efficacy of these therapies.
Keywords: Anti-angiogenic therapy; Cancer; Endothelial; Molecular Pathways; Tumor Angiogenesis; Tumor microenvironment; Vascular targeting.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: None. Consent for publication: Not applicable.. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Angiogenic signaling pathways and anti-angiogenic therapy for cancer.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 May 11;8(1):198. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01460-1. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 37169756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Angiogenic Therapy: Current Challenges and Future Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 5;22(7):3765. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073765. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33916438 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma: mechanisms and anti-angiogenic therapies.Cancer Biol Med. 2023 Jan 12;20(1):25-43. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2022.0449. Cancer Biol Med. 2023. PMID: 36647777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Broad targeting of angiogenesis for cancer prevention and therapy.Semin Cancer Biol. 2015 Dec;35 Suppl(Suppl):S224-S243. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.01.001. Epub 2015 Jan 16. Semin Cancer Biol. 2015. PMID: 25600295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Angiogenesis in Cancer Therapy: Moving Beyond Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor.Oncologist. 2015 Jun;20(6):660-73. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2014-0465. Epub 2015 May 22. Oncologist. 2015. PMID: 26001391 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of p66Shc in Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications.J Cell Mol Med. 2025 Jul;29(14):e70737. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70737. J Cell Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40690563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA‑21: A potential therapeutic target in lung cancer (Review).Int J Oncol. 2025 Aug;67(2):67. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2025.5773. Epub 2025 Jul 11. Int J Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40641110 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Conway EM, Collen D, Carmeliet P. Molecular mechanisms of blood vessel growth. Cardiovasc Res. 2001;49:507–21. - PubMed
-
- Xu N, Li L, Zou J, Yue W, Wang P, Chai M, Li L, Zhang L, Li X, Cheng Y, Wang Z, Wang X, Wang R, Xiang J, Linghu E, Chai N. PRP improves the outcomes of autologous skin graft transplantation on the esophagus by promoting angiogenesis and inhibiting fibrosis and inflammation. J Transl Int Med. 2024;12:384–94. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

