Efficacy and safety of low-dose atorvastatin plus ezetimibe for primary hypercholesterolemia: A randomized, double-blind, multicenter phase 3 trial
- PMID: 40251695
- PMCID: PMC12434550
- DOI: 10.1002/lipd.12442
Efficacy and safety of low-dose atorvastatin plus ezetimibe for primary hypercholesterolemia: A randomized, double-blind, multicenter phase 3 trial
Abstract
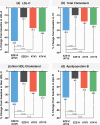
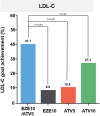
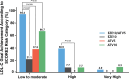
Studies have suggested that low-dose statin monotherapy may be insufficient for target LDL-C levels. In this randomized, double-blind, multicenter phase 3 trial, we evaluated the efficacy of combined ezetimibe and low-dose atorvastatin in 222 Korean patients with primary hypercholesterolemia. Participants received either 10-mg ezetimibe/5-mg atorvastatin (EZE10/ATV5), 10-mg ezetimibe (EZE10), 5-mg atorvastatin (ATV5), or 10-mg atorvastatin (ATV10). At 8 weeks, EZE10/ATV5 achieved the greatest LDL-C reduction (-44.8%) compared with EZE10 (-12.7%, p < 0.0001), ATV5 (-27.3%, p < 0.0001), and ATV10 (-32.0%, p = 0.0012). The combination therapy showed the highest LDL-C goal achievement rate (41.1% vs. EZE10 8.9%, p < 0.0001; ATV5 10.9%, p < 0.0001; ATV10 27.3%, p = 0.0342), particularly in moderate to high-risk patients. Additionally, EZE10/ATV5 had the lowest adverse events among all groups (6.9% vs. 15.0%, 12.3%, and 27.6%, p = 0.017), with most events being mild. These findings suggest that the combination of ezetimibe and low-dose atorvastatin provides superior lipid-lowering efficacy with an improved safety profile, offering an effective treatment for primary hypercholesterolemia in Korean patients.
Keywords: LDL; atorvastatin; clinical trial; ezetimibe; hypercholesterolemia; lipoprotein; phase III.
© 2025 The Author(s). Lipids published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of AOCS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Conard SE, Bays HE, Leiter LA, Bird SR, Rubino J, Lowe RS, et al. Efficacy and safety of ezetimibe added on to atorvastatin (20 mg) versus uptitration of atorvastatin (to 40 mg) in hypercholesterolemic patients at moderately high risk for coronary heart disease. Am J Cardiol. 2008;102(11):1489–1494. 10.1016/j.amjcard.2008.09.075 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

