Giant Dipole Moments: Remarkable Effects Mono-, Di-, and Tri- Hydrated 5,6-Diaminobenzene-1,2,3,4-Tetracarbonnitrile
- PMID: 40251860
- PMCID: PMC12008715
- DOI: 10.1002/jcc.70105
Giant Dipole Moments: Remarkable Effects Mono-, Di-, and Tri- Hydrated 5,6-Diaminobenzene-1,2,3,4-Tetracarbonnitrile
Abstract
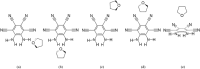
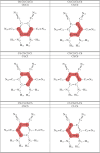
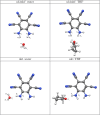
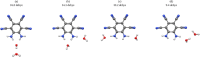
The molecule 5,6-diaminobenzene-1,2,3,4-tetracarbonnitrile (MOI) was first synthesized by Müllen and coworkers in 2016 and boasts an ultrastrong dipole moment of Debye in THF. Gas phase DFT computations do not fully reflect this ultrastrong dipole moment, demonstrating the role of solvent in increasing this dipole moment. Here, we investigate the effect of solvent molecule position on the dipole moment of this species, computationally examining systems with giant dipole moments. These systems are optimized in the gas phase with the B3LYP functional, employing the aug-cc-pVTZ and def2-TZVP basis sets, as well as the B3LYP-D3BJ/aug-cc-pVTZ functional in Orca. Single point DLPNO-CCSD/aug-cc-pVDZ results were obtained from Orca and Psi4, as well as DLPNO-CCSD(T)/CBS information from Psi4. Additionally, these are compared to the dipole moments of di- and tri-hydrated systems, and the SMD models for THF and water at the B3LYP/aug-cc-pVTZ level of theory. The dissociation energies, HOMO-LUMO energy gaps, and dipole moments are presented. These metrics show the nh1nh1' THF system boasts the largest dissociation energy and dipole moment of the singly solvated systems, due to its strong hydrogen bonding. The importance of solvent placement is highlighted and may guide the synthesis of macromolecules or organic frameworks incorporating the MOI or MOI-like subunits. Remarkably, a single solvent molecule provides a good model for the difference between the gas phase and solvated species. The predicted gas phase dipole moments computed with B3LYP/aug-cc-pVTZ for the MOI, its monohydrated complex, dihydrated complex, and its trihydrated complex are 9.6, 14.2, 16.0, and 16.8 Debye, respectively.
Keywords: dipole; energies; hydrogen bonding; solvent.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Computational Chemistry published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


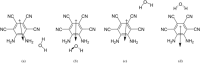



References
-
- Buckingham A. D., “Molecular Quadrupole Moments,” Quarterly Reviews, Chemical Society 13 (1959): 183–214.
-
- Riley K. E. and Hobza P., “On the Importance and Origin of Aromatic Interactions in Chemistry and Biodisciplines,” Accounts of Chemical Research 46 (2013): 927–936. - PubMed
-
- Horiuchi S. and Tokura Y., “Organic Ferroelectrics,” Nature Materials 7 (2008): 357–366. - PubMed
-
- Liao Y., Firestone K. A., Bhattacharjee S., et al., “Linear and Nonlinear Optical Properties of a Macrocyclic Trichromophore Bundle With Parallel‐Aligned Dipole Moments,” Journal of Physical Chemistry B 110 (2006): 5434–5438. - PubMed
-
- Laidler K. J. and Landskroener P. A., “The Influence of the Solvent on Reaction Rates,” Transactions of the Faraday Society 52 (1956): 200.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

