JNK kinase promotes inflammatory responses by inducing the expression of the inflammatory amplifier TREM1 during influenza a virus infection
- PMID: 40253010
- PMCID: PMC12033962
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virusres.2025.199577
JNK kinase promotes inflammatory responses by inducing the expression of the inflammatory amplifier TREM1 during influenza a virus infection
Abstract
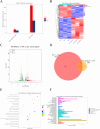
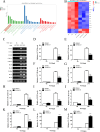
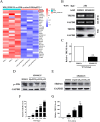
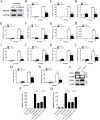
Since the twentieth century, four influenza pandemics caused by IAV have killed millions of people worldwide. IAV infection could induce acute lung injury mediated by cytokine storms, which is an essential cause of death in critically ill patients. Consequently, it is crucial to explore the regulators and regulatory mechanisms of cytokine storms, which may provide potential drug targets and expand our understanding of acute lung injury. Previous studies have shown that JNK kinase is essential in promoting inflammatory responses during viral infections. In this study, we demonstrated that JNK kinase could regulate the IAV-induced cytokine storms by affecting the expression of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory factors. Further studies revealed that inhibition of JNK kinase activity significantly downregulated the expression of the inflammatory amplifier TREM1. Besides, TREM1 knockdown could significantly inhibit the expression of pro-inflammatory factors. Furthermore, SP600125 is a specific inhibitor of JNK kinase. The results show that TREM1 overexpression reversed the effect of SP600125 treatment on the expression of pro-inflammatory factors. Together, we found that JNK kinase could activate the inflammatory amplifier TREM1 to promote inflammatory responses during influenza A virus infection. These findings may provide some inspiration for subsequent researchers to explore the regulatory mechanisms of cytokine storms induced by emerging viral infections.
Keywords: Inflammatory amplifier; Inflammatory responses; Influenza A virus; JNK kinase; TREM1.
Copyright © 2025. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Innate immune role of IL-6 in influenza a virus pathogenesis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Jul 7;15:1605446. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1605446. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40692679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Damage sensing through TLR9 regulates inflammatory and antiviral responses during influenza infection.Mucosal Immunol. 2025 Jun;18(3):537-548. doi: 10.1016/j.mucimm.2025.01.008. Epub 2025 Jan 28. Mucosal Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39884393 Free PMC article.
-
RIG-I agonist SLR10 promotes macrophage M1 polarization during influenza virus infection.Front Immunol. 2023 Jul 5;14:1177624. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1177624. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37475869 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR editing of candidate host factors that impact influenza A virus infection.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Mar 4;13(3):e0262724. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02627-24. Epub 2025 Jan 31. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 39887213 Free PMC article.
-
Physical interventions to interrupt or reduce the spread of respiratory viruses.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jan 30;1(1):CD006207. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006207.pub6. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36715243 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Colonna M. TREMs in the Immune System and beyond. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003;3(6):445–453. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

