The pathogenesis and therapeutic implications of metabolic reprogramming in renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 40253354
- PMCID: PMC12009291
- DOI: 10.1038/s41420-025-02479-9
The pathogenesis and therapeutic implications of metabolic reprogramming in renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
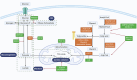
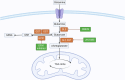
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC), a therapeutically recalcitrant genitourinary malignancy, exemplifies the profound interplay between oncogenic signaling and metabolic adaptation. Emerging evidence positions metabolic reprogramming as a central axis of RCC pathogenesis, characterized by dynamic shifts in nutrient utilization that transcend canonical Warburg physiology to encompass lipid anabolism, glutamine auxotrophy, and microenvironment-driven metabolic plasticity. This orchestrated rewiring of cellular energetics sustains tumor proliferation under hypoxia while fostering immunosuppression through metabolite-mediated T cell exhaustion and myeloid-derived suppressor cell activation. Crucially, RCC exhibits metabolic heterogeneity across histological subtypes and intratumoral regions-a feature increasingly recognized as a determinant of therapeutic resistance. Our review systematically deciphers the molecular architecture of RCC metabolism, elucidating how VHL/HIF axis mutations, mTOR pathway dysregulation, and epigenetic modifiers converge to reshape glucose flux, lipid droplet biogenesis, and amino acid catabolism. We present novel insights into spatial metabolic zonation within RCC tumors, where pseudohypoxic niches engage in lactate shuttling and cholesterol efflux to adjacent vasculature, creating pro-angiogenic and immunosuppressive microdomains. Therapeutically, we evaluate first-in-class inhibitors targeting rate-limiting enzymes in de novo lipogenesis and glutamine metabolism, while proposing biomarker-driven strategies to overcome compensatory pathway activation. We highlight the synergy between glutaminase inhibitors and PD-1 blockade in reinvigorating CD8+ T cell function, and the role of lipid-loaded cancer-associated fibroblasts in shielding tumors from ferroptosis. Finally, we outline a translational roadmap integrating multi-omics profiling, functional metabolomics, and spatial biology to match metabolic vulnerabilities with precision therapies.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The 'Achilles Heel' of Metabolism in Renal Cell Carcinoma: Glutaminase Inhibition as a Rational Treatment Strategy.Kidney Cancer. 2019 Feb 5;3(1):15-29. doi: 10.3233/KCA-180043. Kidney Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30854496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PI3K/AKT/mTOR Dysregulation and Reprogramming Metabolic Pathways in Renal Cancer: Crosstalk with the VHL/HIF Axis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 7;24(9):8391. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098391. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37176098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ferroptosis-associated genes and compounds in renal cell carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 27;15:1473203. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1473203. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39399506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel drugs that target the metabolic reprogramming in renal cell cancer.Cancer Metab. 2016 Jul 13;4:14. doi: 10.1186/s40170-016-0154-8. eCollection 2016. Cancer Metab. 2016. PMID: 27418963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glutaminase and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors suppress pyrimidine synthesis and VHL-deficient renal cancers.J Clin Invest. 2017 May 1;127(5):1631-1645. doi: 10.1172/JCI87800. Epub 2017 Mar 27. J Clin Invest. 2017. PMID: 28346230 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Protein modifications by advanced glycation end products (AGEs) in human clear cell renal cell carcinoma.J Transl Med. 2025 Aug 14;23(1):914. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06958-6. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40813989 Free PMC article.
-
The Metabolic Landscape of Cancer Stem Cells: Insights and Implications for Therapy.Cells. 2025 May 15;14(10):717. doi: 10.3390/cells14100717. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40422220 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Voelker R. What is renal cell carcinoma? JAMA. 2025;333:644. - PubMed
-
- Liao C, Hu L, Zhang Q. Von Hippel-Lindau protein signalling in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Nat Rev Urol. 2024;21:662–675. - PubMed
-
- Ciccarese C, Strusi A, Arduini D, Russo P, Palermo G, Foschi N, et al. Post nephrectomy management of localized renal cell carcinoma. From risk stratification to therapeutic evidence in an evolving clinical scenario. Cancer Treat Rev. 2023;115:102528. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

