Assessment of LASER- induced precipitation of MTA-nanoparticles on root canal dentin surface
- PMID: 40253367
- PMCID: PMC12009375
- DOI: 10.1038/s41405-025-00322-y
Assessment of LASER- induced precipitation of MTA-nanoparticles on root canal dentin surface
Abstract
Aim of the study: This study aims to evaluate the effectiveness of a 980-nm diode laser in inducing mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) nanoparticle precipitation on root canal dentin surfaces for dentinal coverage.
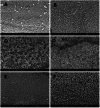
Materials and methods: Sixty mature single-rooted teeth were decoronated at a fixed length of 16 mm and instrumented to size #40/0.04. Canals were filled with either distilled water or nanoMTA suspension and randomly divided based on the treatment modality into: G I and G II flooded with distilled water and laser irradiated at 2 Watt and 4 Watt respectively, GIII and GIV flooded with nanoMTA suspension and laser irradiated at 2 Watt and 4 Watt respectively, G V, flooded with nanoMTA suspension without laser irradiation, and G VI flooded with distilled water without laser irradiation. All samples were longitudinally split and scanned by environmental scanning electron microscopy (ESEM) to evaluate dentinal tubule (DT) occlusion and MTA surface precipitation. Image J analysis software was used to quantify open DTs, while a scoring system assessed dentine coverage.
Results: Laser irradiation significantly enhanced nanoMTA precipitation and dentinal tubule occlusion. The highest dentinal surface coverage, indicated by the lowest pixel percentage, was in laser-irradiated nanoMTA suspension groups G IV (3.4 ± 3.1) and G III (16.7 ± 3), while the lowest coverage was in the non-irradiated saline group G VI (53.4 ± 9.6) (p < 0.05). Median dentinal coverage scores were also highest in G III and G IV (both = 4). G VI showed the least dentinal occlusion, with a statistically significant difference from other groups (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: The 980-nm diode laser effectively enhances MTA nanoparticle precipitation on root canal surfaces, improving dentinal tubule occlusion and sealing potential. Further research is warranted to optimize laser parameters, MTA suspension ratios and to assess clinical outcomes.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: No conflicts of interest. The study at hand was reviewed and the ethical approval was obtained by the Institutional Review Board Organization IORG0010868, Faculty of Oral and Dental Medicine, Ahram Canadian University under the Number: IRB00012891#56. Consent to participate was not required for this study as it was conducted ex vivo on extracted teeth.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An in-vitro evaluation of the effect of 980 nm diode laser irradiation on intra-canal dentin surface and dentinal tubule openings after biomechanical preparation: Scanning electron microscopic study.Indian J Dent. 2015 Apr-Jun;6(2):85-90. doi: 10.4103/0975-962X.155889. Indian J Dent. 2015. PMID: 26097338 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy and Er,Cr:YSGG laser-activated irrigation on dentinal tubule penetration of MTA-based root canal sealer: a confocal microscopy study.Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2021 Dec;36:102584. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2021.102584. Epub 2021 Oct 16. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2021. PMID: 34666196
-
Dynamic intratubular biomineralization following root canal obturation with pozzolan-based mineral trioxide aggregate sealer cement.Scanning. 2016 Jan-Feb;38(1):50-6. doi: 10.1002/sca.21240. Epub 2015 Jul 14. Scanning. 2016. PMID: 26179659 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of laser irradiation on root canal walls after final irrigation with 17% EDTA or BioPure MTAD: X-ray diffraction and SEM analysis.Quintessence Int. 2012 Nov-Dec;43(10):e127-34. Quintessence Int. 2012. PMID: 23115771
-
Comparison of dentin root canal permeability and morphology after irradiation with Nd:YAG, Er:YAG, and diode lasers.Lasers Med Sci. 2010 Sep;25(5):755-60. doi: 10.1007/s10103-010-0775-z. Epub 2010 Apr 27. Lasers Med Sci. 2010. PMID: 20422240
References
-
- Yuliatun L, Kunarti ES, Widjijono W, Nuryono N. Enhancing compressive strength and dentin interaction of mineral trioxide aggregate by adding SrO and hydroxyapatite. Indones J Chem. 2022;22:1651–62. 10.22146/ijc.76231.
-
- Martins MD, Coelho FH, Moreira MS, Marques MM, Pilar EFS, Palo RM, et al. Cytotoxicity, biocompatibility and osteoinductive profile of an MTA-hydrogel-based cement: An in vitro and animal study. Int Endod J. 2023;56:955–67. 10.1111/iej.13929. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

