Evaluating the impact of gut microbiota, circulating cytokines and plasma metabolites on febrile seizure risk in Mendelian randomization study
- PMID: 40253491
- PMCID: PMC12009294
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-97759-w
Evaluating the impact of gut microbiota, circulating cytokines and plasma metabolites on febrile seizure risk in Mendelian randomization study
Abstract
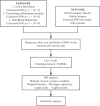
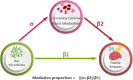
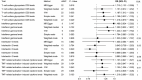
Febrile seizures (FS) is the most common type of convulsion in infants and preschool children. This study aimed to investigate the associations between gut microbiota abundance, plasma metabolites, circulating cytokines, and FS. Summary statistics of 211 gut microbiota traits, 1,400 plasma metabolite traits, 91 circulating cytokine traits, and FS were obtained from publicly available genome-wide association studies. Two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis and causality was inferred using Inverse variance-weighted (IVW), Weighted median, MR-Egger, simple mode-based estimate and weighted mode-based estimate 5 methods. Several sensitivity analyses were also used to ensure the robustness of the results. Furthermore, mediation analysis was used to determine the pathway from gut microbiota to FS mediated by plasma metabolites and circulating cytokines. MR revealed the associations of 1 gut microbiota (phylum Verrucomicrobia), 4 circulating cytokines and 50 plasma metabolites on FS. Based on the known pathogenic metabolites, we observed that the tryptophan, androgen, and sphingolipids pathways are associated with FS. Mediation analysis revealed 1 strongly documented plasma metabolite (Ascorbic acid 2-sulfate) as a mediator linking "gut microbiota to plasma metabolite to FS". Sensitivity analysis was represented no heterogeneity or pleiotropy in this study.Our study provides some causal evidence concerning the effects of the gut microbiota, circulating cytokines, and plasma metabolites on FS, which needs to be verified in randomized controlled trials. These biomarkers provide new insights into the underlying mechanisms of FS and contribute to its prevention, diagnosis, and treatment.
Keywords: Circulating cytokines; Febrile seizures; Gut microbiota; Mediation analysis; Mendelian randomization; Plasma metabolites.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Gould, L., Delavale, V., Plovnick, C., Wisniewski, T. & Devinsky, O. Are brief febrile seizures benign? A systematic review and narrative synthesis. Epilepsia64, 2539–2549 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Mewasingh, L. D., Chin, R. F. M. & Scott, R. C. Current Understanding of febrile seizures and their long-term outcomes. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol.62, 1245–1249 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Fan, Y. & Pedersen, O. Gut microbiota in human metabolic health and disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol.19, 55–71 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Hu, B. et al. Changes of serum metabolomics and gut microbiota reveal specific characteristics of children with febrile seizures. Eur. J. Neurol.30, 3516–3528 (2022). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2023-180/Research Project Supported by Shanxi Scholarship Council of China
- 2023-180/Research Project Supported by Shanxi Scholarship Council of China
- 2023-180/Research Project Supported by Shanxi Scholarship Council of China
- 2023-180/Research Project Supported by Shanxi Scholarship Council of China
- 2023-180/Research Project Supported by Shanxi Scholarship Council of China
- 2023-180/Research Project Supported by Shanxi Scholarship Council of China
- 2021SYS24/Medical Genetics Research Committee Key Laboratory of Shanxi Province "2021 "Four Batch" Science and Technology Innovation Program"
- 2021SYS24/Medical Genetics Research Committee Key Laboratory of Shanxi Province "2021 "Four Batch" Science and Technology Innovation Program"
- 2021SYS24/Medical Genetics Research Committee Key Laboratory of Shanxi Province "2021 "Four Batch" Science and Technology Innovation Program"
- 2021SYS24/Medical Genetics Research Committee Key Laboratory of Shanxi Province "2021 "Four Batch" Science and Technology Innovation Program"
- 2021SYS24/Medical Genetics Research Committee Key Laboratory of Shanxi Province "2021 "Four Batch" Science and Technology Innovation Program"
- 2021SYS24/Medical Genetics Research Committee Key Laboratory of Shanxi Province "2021 "Four Batch" Science and Technology Innovation Program"
- 2023016/Shanxi Province Health and Wellness Committee Funded Project
- 2023016/Shanxi Province Health and Wellness Committee Funded Project
- 2023016/Shanxi Province Health and Wellness Committee Funded Project
- 2023016/Shanxi Province Health and Wellness Committee Funded Project
- 2023016/Shanxi Province Health and Wellness Committee Funded Project
- 2023016/Shanxi Province Health and Wellness Committee Funded Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

