Serum and cord blood neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin levels in pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus and its association with tumor necrosis factor-alpha: A cross-sectional study from Tripura, India
- PMID: 40254320
- PMCID: PMC12010489
- DOI: 10.15537/smj.2025.46.4.20240964
Serum and cord blood neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin levels in pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus and its association with tumor necrosis factor-alpha: A cross-sectional study from Tripura, India
Abstract
Objectives: To examine the significance of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) in women with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) and their correlation with insulin resistance and metabolic markers.
Methods: Blood samples from maternal and cord sources were obtained from 289 pregnant women, divided into GDM, prediabetic, and normal pregnancy groups. Serum levels of NGAL, TNF-α, insulin, fasting blood sugar (FBS), homeostasis model assessment-estimated insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), triglycerides, cholesterol, and so on were measured. Statistical analyses, including the Kruskal-Wallis test and Mann-Whitney U test, were used to compare NGAL levels across patient groups and ethnicities.
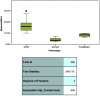
Results: Women with GDM showed significantly higher serum NGAL and TNF-α levels compared to prediabetic and normal pregnancy groups. The NGAL levels positively correlated with key metabolic markers such as FBS, insulin, HOMA-IR, triglycerides, and cholesterol, suggesting a link between elevated NGAL and insulin resistance. In the GDM group, there was also a positive association (r=0.366) between NGAL and TNF-α values. No significant variation in NGAL levels was observed between non-tribal and tribal women.
Conclusion: Elevated levels of NGAL and TNF-α in women with GDM are linked to increased insulin resistance, excessive gestational weight gain, and higher neonatal morbidity risk. These findings underscore the possible involvement of these inflammatory markers in the development of GDM, emphasizing the need for targeted management of both gestational weight gain and inflammation in GDM patients.
Keywords: GDM; NGAL; TNF-α; insulin resistance.
Copyright: © Saudi Medical Journal.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The changes of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in plasma and its expression in adipose tissue in pregnant women with gestational diabetes.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2014 Apr;104(1):136-42. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2014.01.014. Epub 2014 Jan 30. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2014. PMID: 24530115
-
Correlation between circulating level of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and insulin resistance in Nigerian women with gestational diabetes mellitus.Ann Afr Med. 2018 Oct-Dec;17(4):168-171. doi: 10.4103/aam.aam_53_16. Ann Afr Med. 2018. PMID: 30588928 Free PMC article.
-
[Maternal serum tumor necrosis factor-alpha concentration and correlation with insulin resistance in gestational diabetes].Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2004 Nov;39(11):737-40. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2004. PMID: 15634497 Chinese.
-
Serum Levels and Placental Expression of NGAL in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus.Int J Endocrinol. 2020 Jan 3;2020:8760563. doi: 10.1155/2020/8760563. eCollection 2020. Int J Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 32377189 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics and pregnancy outcomes of subtypes of gestational diabetes mellitus based on HOMA-IR and BMI.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2024 Nov;310(5):2355-2361. doi: 10.1007/s00404-024-07733-6. Epub 2024 Sep 17. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2024. PMID: 39287682 Review.
References
-
- Kjeldsen L, Bainton DF, Sengeløv H, Borregaard N.. Identification of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a novel matrix protein of specific granules in human neutrophils. Blood 1994; 83: 799-807. - PubMed
-
- Lou Y, Wu C, Wu M, Xie C, Ren L.. The changes of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in plasma and its expression in adipose tissue in pregnant women with gestational diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2014; 104: 136-142. - PubMed
-
- Bhusal A, Rahman MH, Lee WH, Bae YC, Lee IK, Suk K.. Paradoxical role of lipocalin-2 in metabolic disorders and neurological complications. Biochem Pharmacol 2019; 169: 113626. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous