Quantification of Methylene Blue and Evaluation of Its Pharmacokinetics in ICR Mice by Liquid Chromatography-Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry Using Difluoroacetic Acid
- PMID: 40254552
- PMCID: PMC12009784
- DOI: 10.1002/bmc.70080
Quantification of Methylene Blue and Evaluation of Its Pharmacokinetics in ICR Mice by Liquid Chromatography-Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry Using Difluoroacetic Acid
Erratum in
-
Correction to "Quantification of Methylene Blue and Evaluation of Its Pharmacokinetics in ICR Mice by Liquid Chromatography-Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry Using Difluoroacetic Acid".Biomed Chromatogr. 2025 Jul;39(7):e20000. doi: 10.1002/bmc.70116. Biomed Chromatogr. 2025. PMID: 40375784 No abstract available.
Abstract
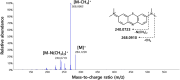
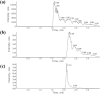
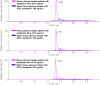
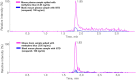
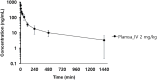
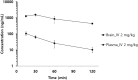
Methylene blue (MB), a phenothiazine derivative, is currently under clinical trials for Alzheimer's disease (AD) due to its potential to inhibit tau aggregation, a key pathological process in AD. In this study, we developed and qualified a rapid and reliable liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (LC-qTOF-MS) method for the quantification of MB in mouse plasma and brain samples. Chromatographic separation was achieved using a PolymerX RP-1 100 Å (50 × 2 mm, 5 μm) column with a mobile phase consisting of water and methanol containing 0.5% difluoroacetic acid, delivered at a flow rate of 0.5 mL/min. Calibration curves were constructed using quadratic regression (weighted 1/concentration2) over a range of 3.05-2222.22 ng/mL in both matrices. The method was successfully applied to characterize the pharmacokinetics of MB in male ICR mice, revealing a high systemic clearance (65.64 mL/min/kg) and substantial brain penetration, as indicated by a brain-to-plasma partition coefficient (Kp,brain) of 23.50 following single intravenous bolus administration. These findings provide critical insights into MB's in vivo behavior and demonstrate the utility of this bioanalytical method for evaluating MB in preclinical studies.
Keywords: LC‐qTOF‐MS; brain penetration; difluoroacetic acid; methylene blue; pharmacokinetics.
© 2025 The Author(s). Biomedical Chromatography published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Simultaneous quantification of methylene blue and its major metabolite, azure B, in plasma by LC-MS/MS and its application for a pharmacokinetic study.Biomed Chromatogr. 2014 Apr;28(4):518-24. doi: 10.1002/bmc.3063. Epub 2013 Oct 14. Biomed Chromatogr. 2014. PMID: 24122875
-
A highly sensitive and rapid LC-MS/MS method for quantification of bexarotene in mouse plasma and brain tissue: Application to mice pharmacokinetic study.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2022 Jan 15;1189:123025. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2021.123025. Epub 2021 Nov 9. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 34840083
-
A reliable LC-MS/MS method for the quantification of N-acetyl-p-benzoquinoneimine, acetaminophen glutathione and acetaminophen glucuronide in mouse plasma, liver and kidney: Method validation and application to a pharmacokinetic study.Biomed Chromatogr. 2018 Nov;32(11):e4331. doi: 10.1002/bmc.4331. Epub 2018 Sep 6. Biomed Chromatogr. 2018. PMID: 29978489
-
Correction to "Quantification of Methylene Blue and Evaluation of Its Pharmacokinetics in ICR Mice by Liquid Chromatography-Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry Using Difluoroacetic Acid".Biomed Chromatogr. 2025 Jul;39(7):e20000. doi: 10.1002/bmc.70116. Biomed Chromatogr. 2025. PMID: 40375784 No abstract available.
-
Liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometric method for the quantification of monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE) and its preclinical pharmacokinetics.Biomed Chromatogr. 2020 Aug;34(8):e4855. doi: 10.1002/bmc.4855. Epub 2020 May 28. Biomed Chromatogr. 2020. PMID: 32304111
References
-
- Akihiko Takashima, B. W. L. B. (2020). Tau Biology. In Vol. 01184. Retrieved from https://library.cnu.ac.kr/eds/detail/edsebk_2380267.
-
- Burhenne, J. , Riedel K. D., Rengelshausen J., et al. 2008. “Quantification of Cationic Anti‐Malaria Agent Methylene Blue in Different Human Biological Matrices Using Cation Exchange Chromatography Coupled to Tandem Mass Spectrometry.” Journal of Chromatography. B, Analytical Technologies in the Biomedical and Life Sciences 863, no. 2: 273–282. 10.1016/j.jchromb.2008.01.028. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

