Shikonin attenuates blood-brain barrier injury and oxidative stress in rats with subarachnoid hemorrhage by activating Sirt1/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling
- PMID: 40254555
- PMCID: PMC12012320
- DOI: 10.4196/kjpp.24.182
Shikonin attenuates blood-brain barrier injury and oxidative stress in rats with subarachnoid hemorrhage by activating Sirt1/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling
Abstract
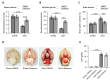
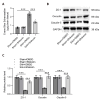
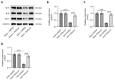
Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is a serious intracranial hemorrhage characterized by acute bleeding into the subarachnoid space. The effects of shikonin, a natural compound from the roots of Lithospermum erythrorhizon, on oxidative stress and blood-brain barrier (BBB) injury in SAH was evaluated in this study. A rat model of SAH was established by endovascular perforation to mimic the rupture of intracranial aneurysms. Rats were then administered 25 mg/kg of shikonin or dimethylsulfoxide after surgery. Brain edema, SAH grade, and neurobehavioral scores were measured after 24 h of SAH to evaluate neurological impairment. Concentrations of the oxidative stress markers superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione (GSH), and malondialdehyde (MDA) in the brain cortex were determined using the corresponding commercially available assay kits. Evans blue staining was used to determine BBB permeability. Western blotting was used to quantify protein levels of tight junction proteins zonula occludens-1, Occludin, and Claudin-5. After modeling, the brain water content increased significantly whereas the neurobehavioral scores of rats with SAH decreased prominently. MDA levels increased and the levels of the antioxidant enzymes GSH and SOD decreased after SAH. These changes were reversed after shikonin administration. Shikonin treatment also inhibited Evans blue extravasation after SAH. Furthermore, reduction in the levels of tight junction proteins after SAH modeling was rescued after shikonin treatment. In conclusion, shikonin exerts a neuroprotective effect after SAH by mitigating BBB injury and inhibiting oxidative stress in the cerebral cortex.
Keywords: Antioxidants; Blood-brain barrier; Subarachnoid hemorrhage; Tight junctions; Traditional Chinese medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
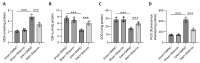
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of Rho kinase by hydroxyfasudil attenuates brain edema after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats.Neurochem Int. 2012 Feb;60(3):327-33. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2011.12.014. Epub 2011 Dec 30. Neurochem Int. 2012. PMID: 22226843 Free PMC article.
-
Geniposide attenuates early brain injury by inhibiting oxidative stress and neurocyte apoptosis after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Jul;49(7):6303-6311. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07438-6. Epub 2022 Apr 26. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35474057
-
Amelioration of oxidative stress and protection against early brain injury by astaxanthin after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage.J Neurosurg. 2014 Jul;121(1):42-54. doi: 10.3171/2014.2.JNS13730. Epub 2014 Apr 11. J Neurosurg. 2014. PMID: 24724856
-
GPR30 alleviated subarachnoid hemorrhage-induced blood-brain barrier dysfunction by activating the PI3K/Akt and Nrf2/HO-1 pathways.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024 Jul 1;327(1):C65-C73. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00035.2024. Epub 2024 May 20. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38766766
-
TSG-6 Attenuates Oxidative Stress-Induced Early Brain Injury in Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Partly by the HO-1 and Nox2 Pathways.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2020 Dec;29(12):104986. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2020.104986. Epub 2020 Sep 8. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2020. PMID: 32992175

