Percutaneous mechanical circulatory support for acute right heart failure: A practical approach
- PMID: 40254772
- PMCID: PMC12287799
- DOI: 10.1002/ehf2.15305
Percutaneous mechanical circulatory support for acute right heart failure: A practical approach
Abstract
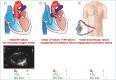
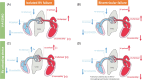
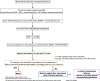
Acute right heart failure (RHF) represents a critical entity with significant morbidity and mortality. This review examines the role of percutaneous right ventricular assist devices (pRVADs) as a cornerstone of therapy in cases refractory to conventional management. Devices such as the Impella RP and dual-lumen cannulas provide targeted haemodynamic support, with indications in various clinical scenarios, including acute myocardial infarction, post-cardiac surgery, myocarditis, and after left ventricular assist device (LVAD) implantation. Successful implementation requires meticulous haemodynamic assessment, including parameters derived from pulmonary artery catheterization and echocardiography, to guide patient selection, optimize device placement, and monitor therapeutic response. The manuscript highlights contemporary weaning strategies, emphasizing recovery of right ventricular function, stabilization of systemic haemodynamics, and restoration of end-organ perfusion. While no universal protocols exist, this review presents a pragmatic framework informed by available evidence and expert consensus. Furthermore, the potential complications of pRVAD use-ranging from thromboembolism and haemolysis to device-specific issues such as migration and tricuspid valve damage-are discussed alongside preventive and management strategies. Key challenges in RHF management, including the interplay between right and left ventricular function, the impact of pulmonary vascular resistance, and the use of adjunctive pulmonary vasodilators, are addressed. The review underscores the absence of durable right ventricular assist devices and the need for innovation to close this therapeutic gap. Multidisciplinary collaboration among intensivists, cardiologists, and cardiac surgeons is critical to optimizing outcomes. This review provides actionable insights to assist clinicians in navigating the complexities of acute RHF, fostering a tailored and evidence-based approach to this high-risk population.
Keywords: Cardiogenic shock; ECMO; Impella; pRVAD.
© 2025 The Author(s). ESC Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
A.C. received consultant and/or speaker fees from Abiomed, Biosensor, Boston Scientific, Medtronic, Menarini, and Shock Wave Medical. B.S. is funded by the Else Kröner‐Fresenius‐Stiftung and received research support from Abiomed and speaker fees from Abiomed and AstraZeneca, outside of the submitted work. C.V. received speaker and research grants from Abiomed. He is funded by the FWO‐Flanders (grant number 1803923N). M.B. is a consultant for Abbott Vascular, Abiomed, Boston Scientific, Cardiovascular Systems, Chiesi, Saranas, and Zoll. P.C.S. received honoraria for lectures/consulting from Novartis, Vifor, Bayer, Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, Cardior, BMS, Abiomed, Pharmacosmos, and Amgen not related to this article and research support for the department from Boehringer Ingelheim, Edwards, and Abiomed not related to this article. All other authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Harjola VP, Mebazaa A, Čelutkiene J, Bettex D, Bueno H, Chioncel O, et al. Contemporary management of acute right ventricular failure: a statement from the Heart Failure Association and the Working Group on Pulmonary Circulation and Right Ventricular Function of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur J Heart Fail 2016;18:226‐241. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.478 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

